Figure 6.
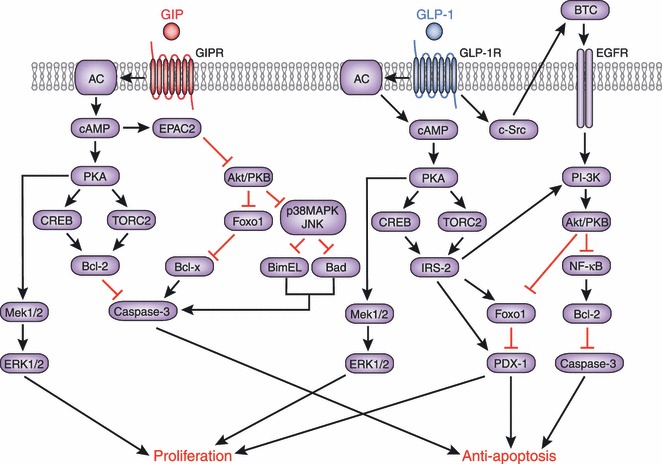
Molecular mechanisms underlying the anti‐apoptotic and proliferative effects of glucose‐dependent insulinotropic polypepide (GIP) and glucagon‐like peptide (GLP)‐1. Signaling cascades linking the GIP receptor (GIPR) and the GLP‐1 receptor (GLP‐1R) with anti‐apoptotic and proliferative effects share similarities and differences as shown. Involvement of epidermal growth factor (EGFR) and phosphoinositide 3‐kinase (PI‐3K) has been shown to be a critical difference between the GIPR‐ and GLP‐1R‐signaling pathways. AC, adenylate cyclase; Akt, v‐akt murine thymoma viral oncogene homolog; Bad, Bcl‐2 antagonist of cell death; Bcl, B‐cell CLL/lymphoma; BimEL, Bcl‐2 interacting mediator of cell death EL; BTC, betacellulin; cAMP, cyclic adenosine monophosphate; CREB, cAMP response element‐binding; c‐Src, proto‐oncogene tyrosine‐protein kinase Src; EPAC2, exchange protein directly activated by cAMP2; ERK, extracellular signal‐regulated kinase; Foxo1, forkhead box protein O1; IRS‐2, insulin receptor substrate 2; JNK, c‐Jun N‐terminal kinase; MAPK, mitogen‐activated protein kinase; Mek, mitogen‐activated protein kinase kinase; NFκB, nuclear factor kappa‐light‐chain‐enhancer of activated B cells; PDX‐1, pancreas/duodenum homeobox protein 1; PKA, protein kinase A; PKB, protein kinase B; TORC2, transducer of regulated CREB activity 2.
