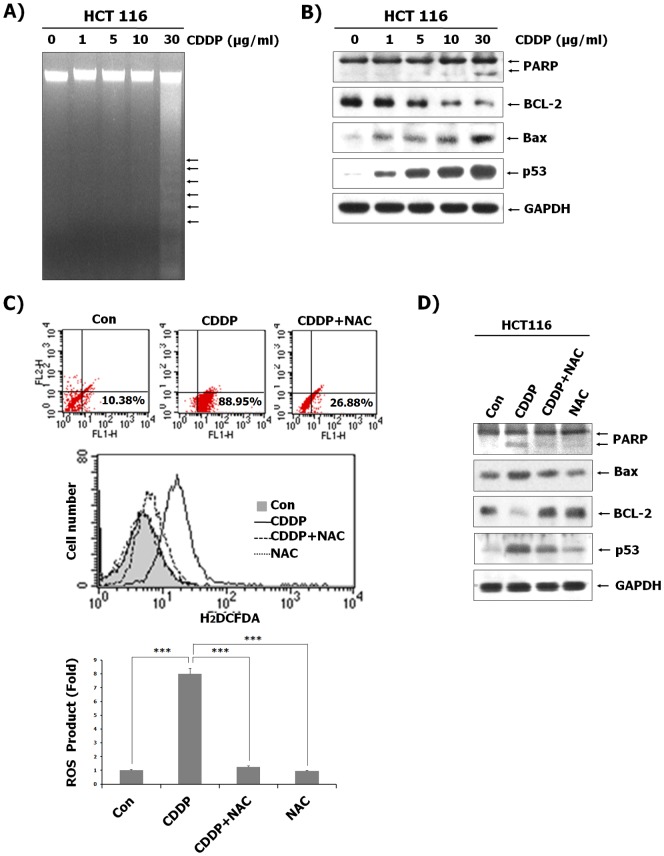
Figure 1. HCT116 cell apoptosis induced by CDDP via a ROS-dependent pathway.
(A) After treatment of CDDP at the indicated concentrations for 24 h, genomic DNA was isolated and separated by electrophoresis on a 2% agarose gel. The DNA was stained with ethidium bromide and visualized under UV light. (B) Total protein from HCT116 cells was isolated, and immunoblotting analysis was performed with the indicated antibodies. (C) HCT116 cells were treated with or without 30 µg/mL CDDP after pre-treatment with 10 nM NAC, followed by the replacement of the culture medium with freshly prepared medium containing 10 µM DCFH-DA. After 30 min of incubation at 37°C, fluorescence intensity was measured by flow cytometry. Results represent the fold increase from their respective controls (cells not treated with CDDP), considered as 1. Data represent the mean ± SD of 3 independent measurements. ***P<0.001 vs. the CDDP-treated control. (D) HCT116 cells were treated with or without CDDP (30 µg/mL) after pre-treatment of NAC (10 nM). Protein was isolated from the cells and analyzed by immunoblotting using indicated antibodies. GAPDH was included as an internal control.