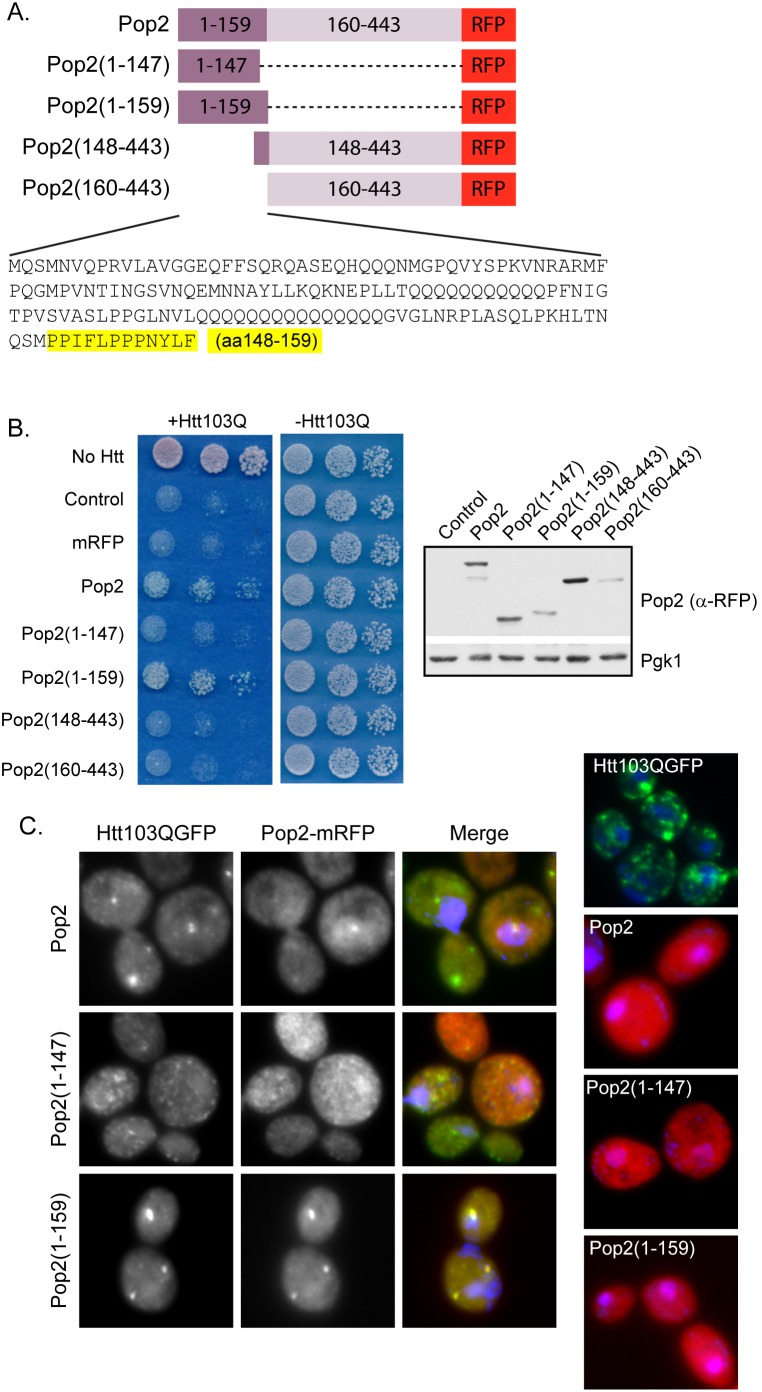
Figure 5. A short proline-rich stretch in the Pop2 polyQ domain is required to impact Htt103Q toxicity and aggregation.
(A) A diagram illustrating the constructs utilized in these experiments and the sequence of the polyQ domain. The proline-rich region of the Pop2 polyQ domain is highlighted. Numbers indicate amino acid residues. (B) Only full length Pop2 and Pop2(1–159) suppress Htt103Q toxicity. Expression of Pop2 constructs was monitored by Western blot detection using an anti-RFP antibody. (C) Pop2 lacking the proline-rich region is unable to alter Htt103Q aggregation as monitored by fluorescence microscopy. Nuclei were visualized with DAPI staining.