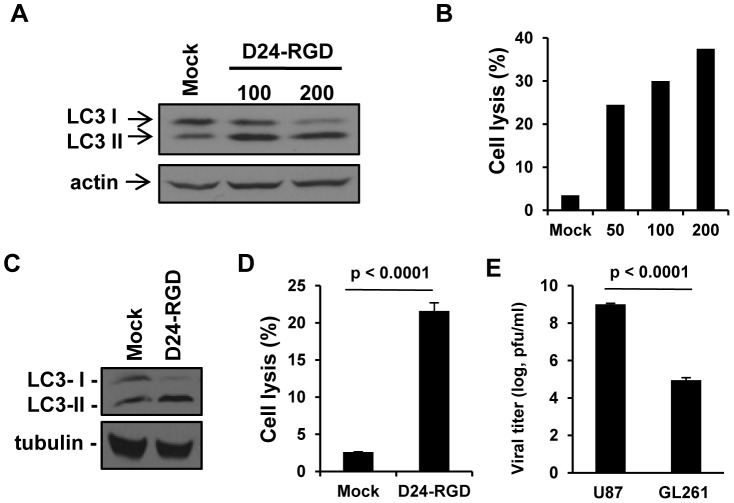
Figure 1. In vitro characterization of Delta-24-RGD-mediated autophagy and anticancer effect in GL261 mouse glioma cells.
A &B. Gl261 cells were infected with Delta-24-RGD (D24-RGD) at the indicated dose (pfu/cell). 72 h later, cell lysates were analyzed by Western Blot for LC3-I to LC3-II conversion (A) and Delta-24-RGD-mediated cell lysis was quantified (B). Actin levels are shown as a protein loading control. C &D. U-87 MG cells were infected with Delta-24-RGD (D24-RGD) at 10 pfu/cell. 72 h later, cell lysates were subjected to Western Blot analysis for LC3-I to LC3-II conversion (C). Tubulin levels are shown as a protein loading control. Delta-24-RGD-mediated cell lysis was quantified (D). P<0.0001 (Student's t-test, double sided). (D). E, Cells were infected with Delta-24-RGD at 10 pfu/cell. 48 h later, viral progeny was quantified in the cultures. P<0.0001 (Student's t-test, double sided). Data are represented as mean ± S.E.; n = 3. Note that cell lyses and viral replication were more efficient in human than in mouse glioma cells.