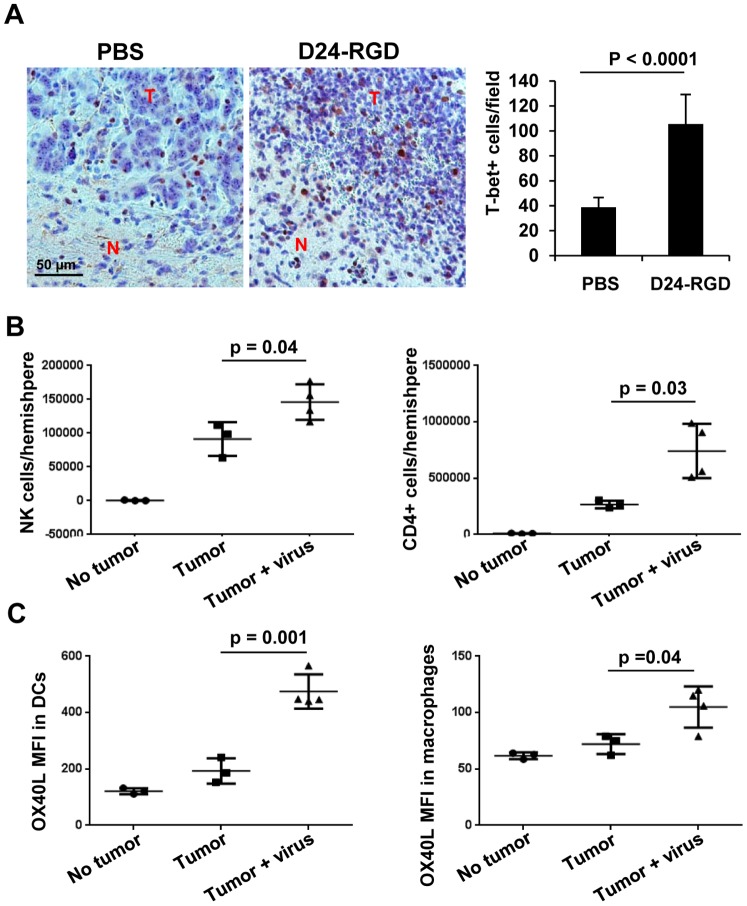
Figure 2. Delta-24-RGD induced immune cells infiltration in GL261 mouse glioma xenografts.
Delta-24-RGD was administered intratumorally on days 7, 9, 11 after GL261 cell intracranial implantation. On day 14 of the experiment, brains were collected and analyzed. The brains were fixed (A) or the leukocytes from fresh hemispheres with or without tumor were isolated and analyzed with flow cytometry (B and C). A. Immunohistochemistry analysis of T-bet expression in paraffin-embedded tumor sections from mice treated with PBS or Delta-24-RGD (D24-RGD) (left panel). T-bet+ cells were quantified and represented as mean ± S.E.; n = 9–10. P<0.0001 (Student's t-test, double sided). (right panel). T: tumor; N: normal brain tissue. B. NK+ cells or CD4+ T cells present in hemispheres with or without tumor were quantified. No tumor: naïve mice; Tumor: GL261-glioma bearing mice; Tumor + virus: Delta-24-RGD-treated GL261-glioma bearing mice. Data are represented as mean ± S.E.; n = 3–4. P<0.05 (Student's t-test, double sided). C. OX40L expression levels in dendritic cells (DC) or macrophages obtained from brains of naïve mice (No tumor), GL261-glioma bearing mice (Tumor), and Delta-24-RGD-treated GL261-glioma bearing mice (Tumor + virus). MFI: mean fluorescence intensity. Data are represented as mean ± S.E.; n = 3–4. P<0.05 (Student's t-test, double sided). Note that increase in T-bet positive cells (cells expressing IFNγ), CD4, and enhanced expression of OX40L in dendritic cells and macrophages strongly indicate a Th1 immunity at the tumor site.