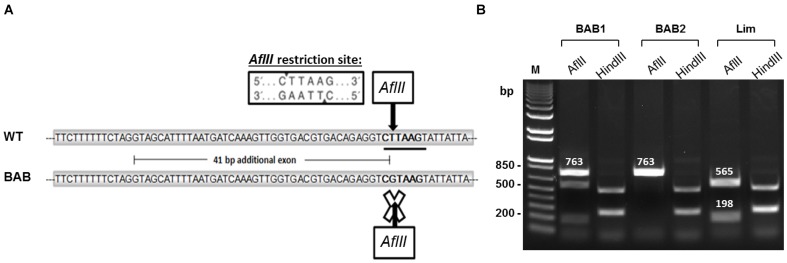
Figure 5. RFLP-PCR genotyping.
(A) The T>G substitution leads to disappearance of the AflII restriction site in Blonde d'Aquitaine (BAB). (B) PCR amplification products from two BAB animals and one Limousine animal (Lim) were digested either by AflII or by HindIII restriction enzymes. AflII digestion differentiates animals which are homozygous G/G (BAB2, no digestion, one 763-bp fragment), heterozygous T/G (BAB1, three fragments: undigested PCR products corresponding to the mutated allele (763-bp) and PCR products corresponding to the wild-type allele gave two 565-bp and 198-bp fragments) or homozygous T/T (Lim, two fragments: 565-bp and 198-bp). HindIII digestion was used as a cutting control. WT: wild-type; M: size marker.