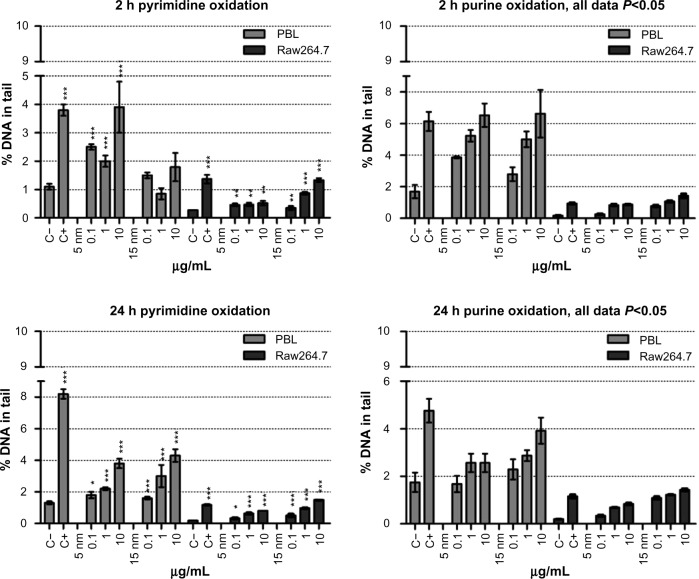
Figure 4.
Oxidative DNA damage evaluated using the enzyme-modified comet assay in PBL and Raw264.7.
Notes: Dose-dependent pyrimidines oxidation was detected in PBL after 24 hours of exposure to 5 nm and 15 nm Au NPs (P=0.05 and P=0.028, respectively). In Raw264.7 the pyrimidines oxidation, detected by the EndoIII enzyme, showed a dose-dependent effect after 2 hours of exposure to 15 nm Au NPs (P=0.035) and at 24 hours to 5 nm and 15 nm Au NPs (P=0.009 and P=0.006, respectively). By Fpg, dose-dependent purines oxidation was observed in PBL after 2 hours of exposure to 5 nm and 15 nm Au NPs (P=0.009 and P=0.007, respectively), as well as after 24 hours of exposure to 5 nm Au NPs (P=0.014). In Raw264.7, a dose-effect relationship was detected following 2 hours of exposure to 15 nm Au NPs (P=0.01) and 24 hours of incubation in the presence of 5 nm Au NPs (P=0.015). Data are shown as mean ± SEM (PBL: n=4; Raw264.7: n=6) of percent DNA in tail. Student’s t-test: *P<0.05; **P<0.01; ***P<0.001.
Abbreviations: Au NP, gold nanoparticle; C+, positive control (10 μM hydrogen peroxide); C−, negative (untreated) control; DNA, deoxyribonucleic acid; EndoIII, endonuclease-III; Fpg, formamidopyrimidine-DNA glycosylase; h, hours; PBL, peripheral blood lymphocytes; SEM, standard error of the mean.