Fig 2. Amygdala structure, circuitry and recording methods.
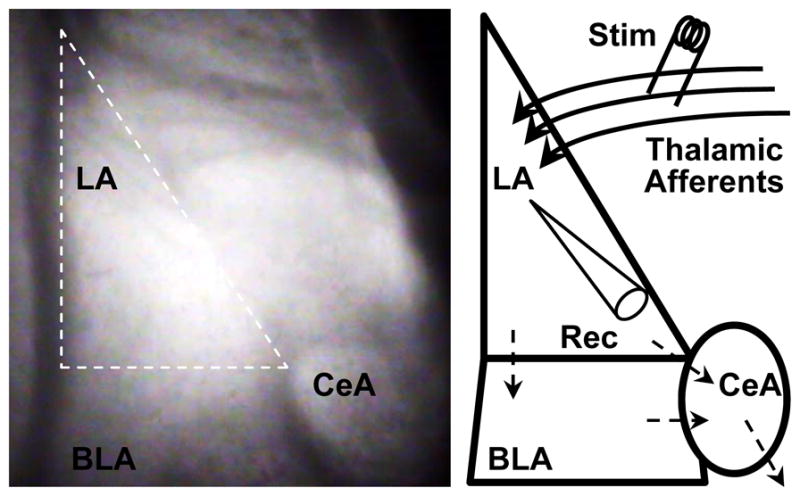
(Left) Infrared differential interference contrast image taken at 40× of a coronal mouse brain slice containing the amygdala. The amygdala is comprised of lateral (LA), basolateral (BLA) and central (CeA) nuclei. We performed our experiments in the LA (outlined in white dashes). (Right) Schematic depicting amygdala nuclei. Thalamic afferent axons enter the LA and synapse onto LA neurons. LA neurons send their projections to the BLA and CeA; the BLA sends its projections to the CeA as well. CeA neurons send their projections to midbrain and brainstem nuclei responsible for evoking the fight or flight response in mammals, which contributes to anxiety-like behaviors and freezing in fear conditioning. We stimulated (Stim) thalamic afferent synapses and recorded post-synaptic responses (Rec; whole cell patch clamp) in LA pyramidal neurons.
