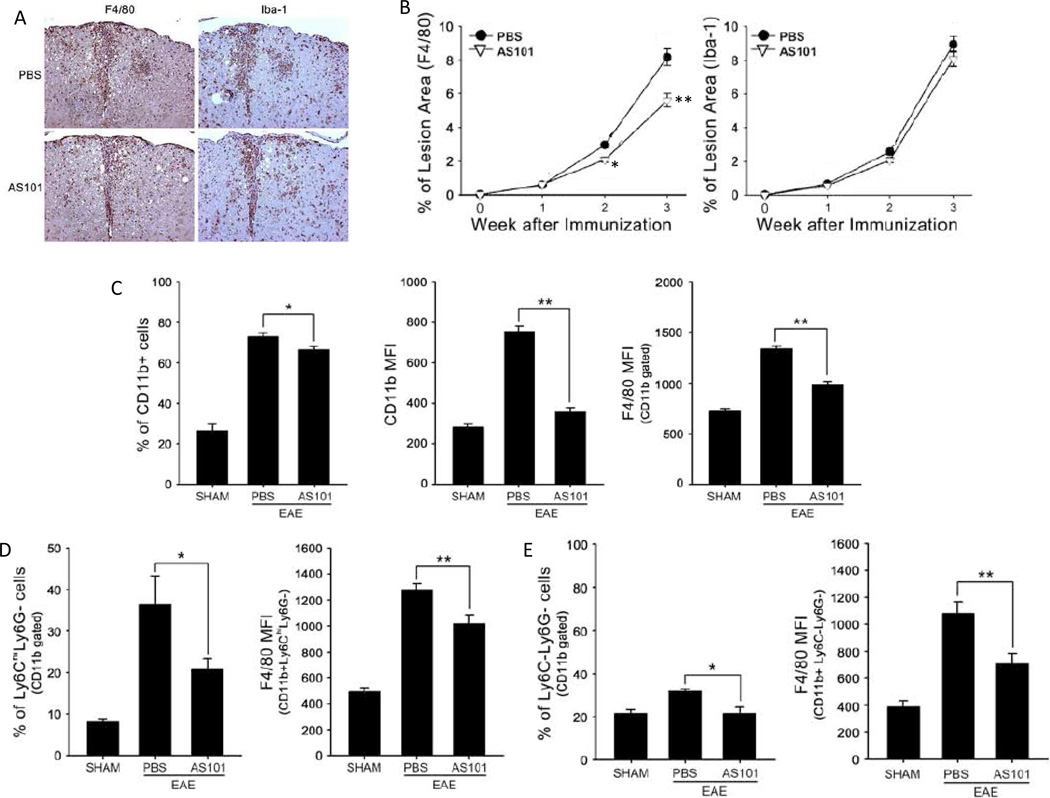
Figure 2.
AS101 inhibits infiltration of pro-inflammatory monocytes/macrophages into the spinal cord in EAE mice. Spinal cords (n = 5–10 per group) were removed on days 7, 14 and 21 post immunization. (A) Representative spinal cord sections from EAE mice treated with PBS oor AS101 immunostained with F4/80 and Iba-1 antibodies (day 14 post immunization). (B) Results of quantification of % of lesion area occupied by F4/80 or Iba-1 immunoreactive cells (n=5 per group). *p<0.05, **p<0.01 compared to corresponding value for PBS-treated mice. (C – E) Mononuclear cells were isolated from spinal cords of mice in the sham, EAE PBS, and EAE AS101 groups (n = 5–10 mice per group). Cells were stained with CD11b, F4/80, Ly6C and Ly6G, then analyzed using flow cytometry. F4/80 expression in the cells is presented as mean fluorescence intensity (MFI). AS101 treatment reduced: the percentage of CD11b+ cells and the number of CD11b-expressing F4/80-positive cells (C), the proportion of inflammatory monocytes and the number of F4/80 expressing cells (D); and the proportion of CD11b+ Ly6C-Ly6G (resident monocyte) (D and E). *p<0.05, **p<0.01.