Figure 1.
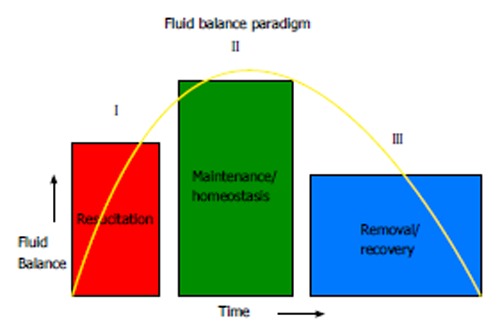
Fluid balance paradigm. The management of fluid therapy in critical illness can be conceptually viewed across three broad phases differentiated according to clinical status of the patient. During the “resuscitation” phase, the goal is restoration of effective intra-vascular volume, organ perfusion and tissue oxygenation. Fluid accumulation and a positive fluid balance may be expected. During the maintenance phase, the goal is maintenance of intravascular volume homeostasis. The broad aim here would be to mitigate excessive fluid accumulation and prevent unnecessary fluid loading. During the recovery phase, passive and/or active fluid removal would correspond to organ recovery.
