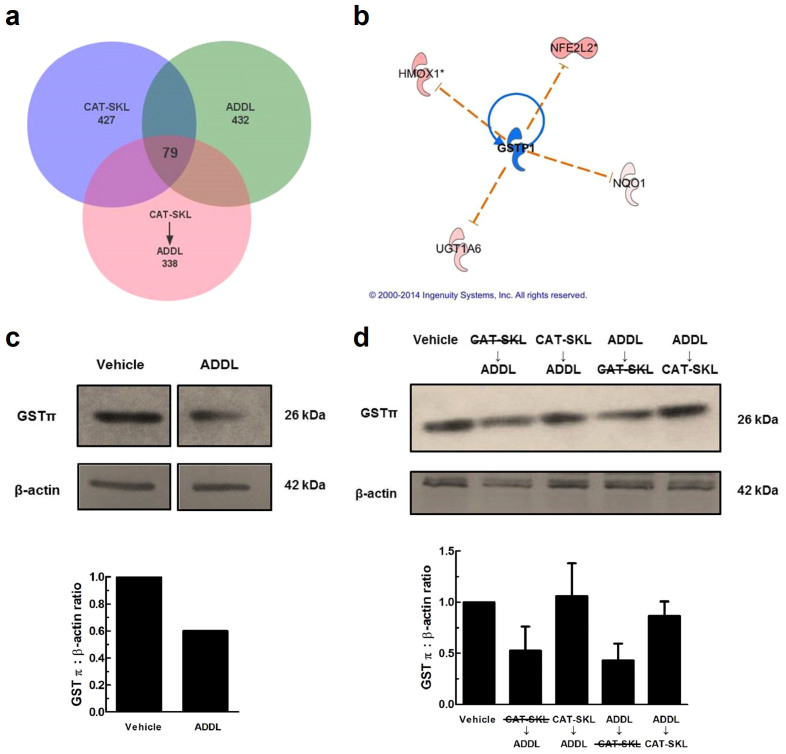
Figure 7. CAT-SKL protects neurons from GSTπ depletion in ADDL treated neurons.
(a) Venn diagram illustrating 79 overlapping genes between treatments. A total of 432 genes were altered in ADDLs, 427 in CAT-SKL, and 338 in CAT-SKL followed by ADDL treatments. Complete lists of genes are available in supplementary Table 1. (b) Upstream regulator analysis was used to identify potential molecules upstream responsible for the observed gene expression changes in the dataset. Blue indicates upstream regulator GSTπ is predicted to be inactivated. Nuclear factor (erythroid-derived 2)-like 2 (NFE2L2) is a transcription factor involved in increasing the expression of various antioxidant enzymes including: heme oxygenase-1 (HMOX1), UDP-glucuronosyltransferase (UGT1A6), and NAD(P)H quinone oxidoreductase 1 (Nqo1), among others. (c) Vehicle and ADDL (1 μM) treated neurons for 24 hours. Bands are taken from same western blot. Quantification of western blots normalized to β-actin. Full-length blots are presented in Supplementary Figure 2c. (d) Lane assignments left to right: Vehicle control: cells pretreated with enzymatically inactive CAT-SKL (1 μM) - indicated with line through for 24 hours, followed by ADDL (1 μM) for 24 hours; cells pretreated with CAT-SKL (1 μM) for 24 hours, followed by ADDL (1 μM) for 24 hours; cells treated with ADDL (1 μM) for 24 hours, followed by enzymatically inactive CAT-SKL (1 μM) for 24 hours; cells treated with ADDL (1 μM) for 24 hours, followed by CAT-SKL (1 μM) for 24 hours. Quantification of western blots normalized to β-actin (n = 3). Full-length blots are presented in Supplementary Figure 2d.