Fig. 3. Localisation of Crb and Chp in wild-type and mutant PRCs.
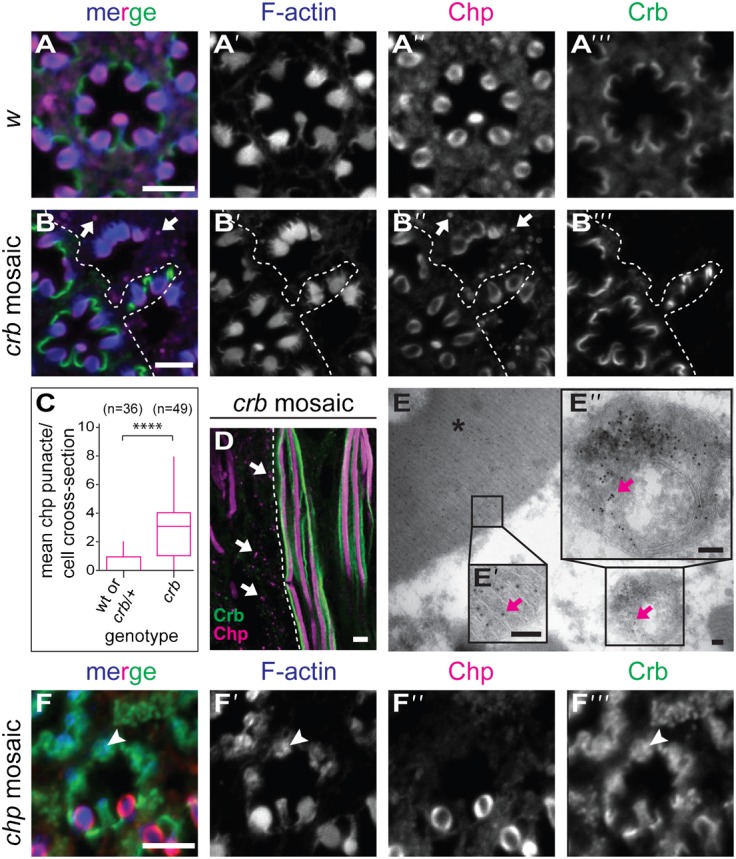
(A,B,D) Drosophila adult ommatidia. Genotypes are w (A), crb11A22 mosaic (B,D,E) and chp2 mosaic (F). Confocal images of immunostainings on tangential (A,B,F) and longitudinal (D) sections of PRCs stained for F-actin (blue), Chp (magenta) and Crb (green). White arrows in panels B,B″ and D point to intracellular Chp punctae in crb mutant cells. (C) Box-plot representing the number of cytosolic Chp positive punctae per cell per cross-section of wt, crb/+ and crb/crb mutant PRCs. Whiskers indicate 5–95% confidence interval. Statistical significance is analysed with Kruskal–Wallis test, followed by Dunn's multiple comparisons test. ****p<0.0001. (E–E″) Immunoelectron micrograph showing the localization of Chp (10 nm gold particle) (magenta arrows) in a cross-section of crb11A22 mutant PRC. Chp is localized in the rhabdomere (E,E′, asterisk) and in a multivesicular body (E″, arrow). (F) Confocal images of immunostainings on tangential sections of PRCs stained for F-actin (blue), Chp (magenta) and Crb (green). White arrowhead points to the apical membrane in chp mutant cells, which is no longer subdivided into rhabdomere and stalk. Scale bars: 5 µm (A,B,D,F), 100 nm (E).
