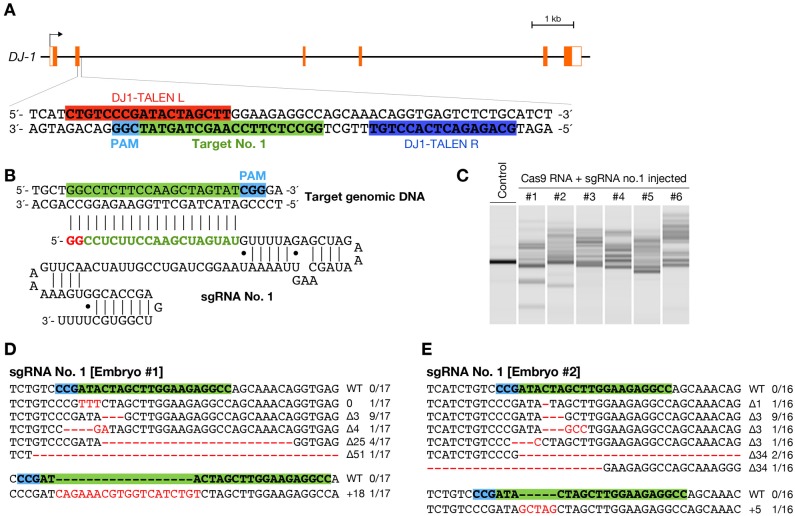
Fig. 1. Induction of somatic mutations with CRISPR/Cas-mediated RGENs.
(A) Schematic representation of the genomic structure of the DJ-1 gene. Coding and untranslated exon regions are shown as solid and open boxes, respectively. The 20-bp target sequence of sgRNA no. 1 is indicated in green box, adjacent to NGG protospacer adjacent motif (PAM) sequence in light blue box. Red and blue boxes indicate the left and right recognition sequence of previously described TALENs (Ansai et al., 2013). (B) The sgRNA sequence for target site no. 1. First 20-nts sequence interacts with the complementary strand of the DNA target site. Red and green letters indicate the sequence required by T7 RNA polymerase and the customizable targeting sequence, respectively. (C) Heteroduplex mobility assay (HMA) in embryos injected with a mixture containing 100 ng/µL of Cas9 RNA and 25 ng/µL of sgRNA no. 1. Multiple heteroduplex bands were shown in PCR amplicons from each the RGEN-injected embryo (#1–6), whereas a single band was shown from each “Control” embryo without injection of the RGENs. (D,E) Subcloned sequences observed in the RGEN-injected embryos #1 (D) and #2 (E). Red dashes and letters indicate the identified mutations. The sgRNA targeting sequence and PAM indicate in green and light blue boxes, respectively. The size of deletions and insertions are shown to the right of each mutated sequence (Δ; deletions, +; insertions). Numbers on the right edge indicate the numbers of mutated clones identified from all analyzed clones from each embryo.