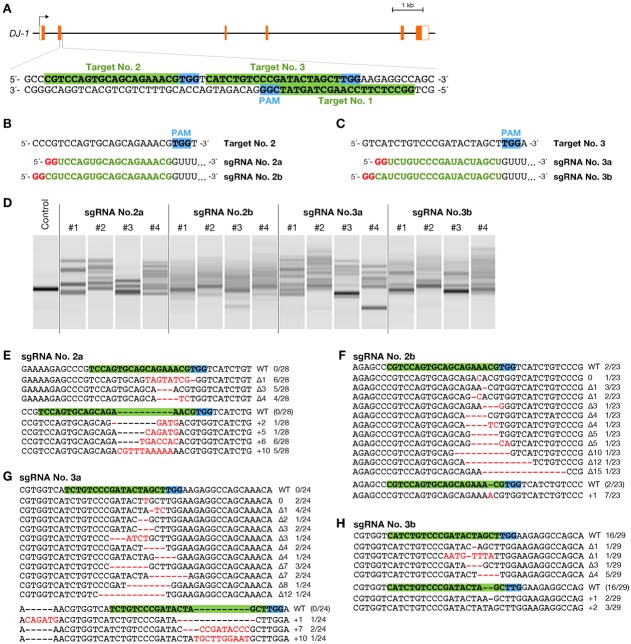
Fig. 2. Somatic mutations induced at genomic sequences not containing GG at the 5′ ends.
(A) Schematic illustration of the additional RGEN targeting sequences on the 2nd exon of DJ-1 gene. Target site no. 2 and 3 do not contain GG at their 5′ ends, while target site no. 1 starts with the sequence GG. The targeting sequence of sgRNA is indicated in green box, adjacent to NGG protospacer adjacent motif (PAM) sequence in light blue box. (B,C) The sequences of sgRNAs for target site no. 2 (B) and 3 (C). Red and green letters indicate the sequence required by T7 RNA polymerase and the customizable targeting sequence, respectively. Two sgRNAs were designed for each target site. The sgRNA no. 2a and 3a contain the 18-nts sequence complementary to their genomic target site, while the sgRNA no. 2b and 3b contain the 20-nts sequence. These sgRNAs also contain 1- or 2-nt mismatches to their genomic target sequence at 5′ end. (D) Heteroduplex mobility assay (HMA) in embryos injected with a mixture containing 100 ng/µL of Cas9 RNA and 25 ng/µL of sgRNA. Multiple heteroduplex bands were shown in PCR amplicons from each the RGEN-injected embryo, whereas a single band was shown from each “Control” embryo without the injection of the RGENs. (E–H) Subcloned sequences observed in the embryos injected with sgRNA no. 2a (E), 2b (F), 3a (G), or 3b (H). Red dashes and letters indicate the identified mutations. The sgRNA targeting sequence and PAM indicate in green and light blue boxes, respectively. The size of deletions and insertions are shown to the right of each mutated sequence (Δ; deletions, +; insertions). Numbers on the right edge indicate the numbers of mutated clones identified from all analyzed clones from each embryo.