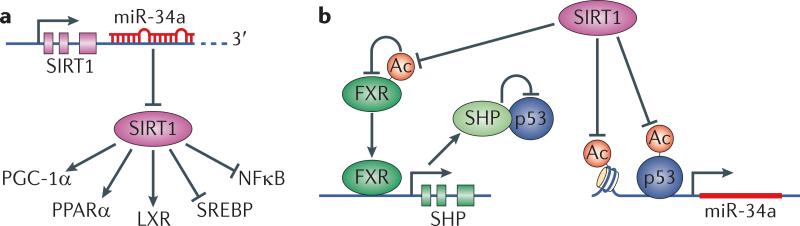
Figure 3. The regulatory loop of miR-34a, SIRT1, FXR and p53.
miR-34a is highly expressed in patients with NAFLD and NASH and type 2 diabetes. On the molecular level, miR-34a has been shown to exert its function through its effect on SIRT1. miR-34a is then in turn inhibited by SIRT1 in a regulatory loop that includes miR-34a, SIRT1, FXR and p53 to affect cholesterol, lipid and energy homeostasis as well as inflammation. A. miR-34a inhibits SIRT1 and reduces its protein level and prevents its activation of PGC-1α, PPARα and LXR (key regulators of cholesterol/lipid/energy homeostasis), and inhibition of SREBP and NF-κB (activators of lipogenesis and cholesterogenesis, and inflammation, respectively). B. SIRT1 feedback inhibits miR-34a in several ways: it deacetylates p53 and inhibits p53-dependent transcriptional activation of miR-34a. In addition, SIRT1 inhibits the miR-34a promoter through histone deacetylation. Finally, SIRT1 deacetylates and activates FXR. FXR transcriptionally activates SHP, which sequesters p53 and thus inhibits miR-34a transcription.