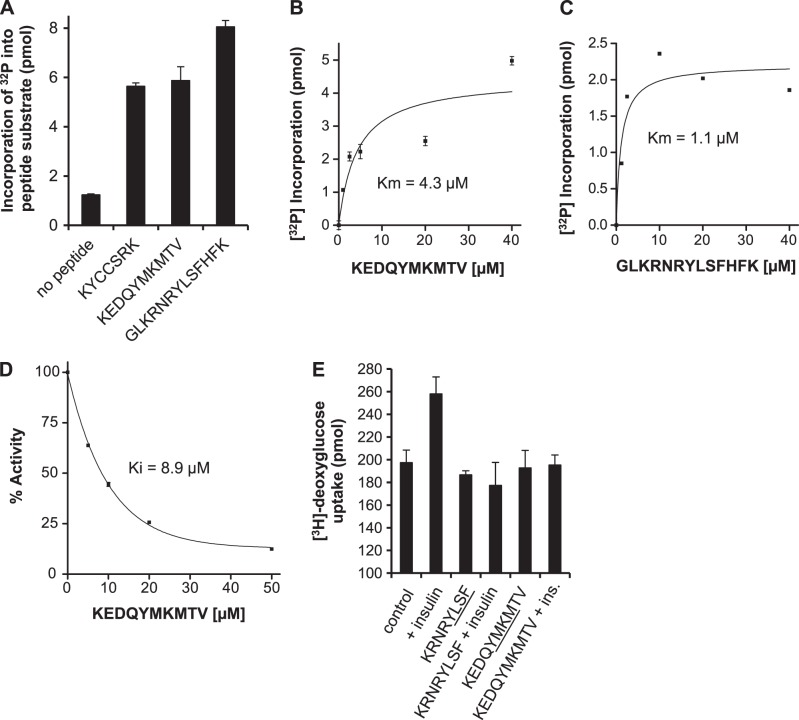
Figure 7.
Identification of hBVR-based peptide inhibitors of IRK activity and glucose uptake. A) IRK phosphorylates hBVR-derived tyrosine-containing peptides. Noted hBVR-based peptides (20 μM) were used as substrates in IRK assays in vitro, and incorporation of [32P] into peptide was measured. B) KEDQYMKMTV is a high-affinity substrate for IRK. IRK was assayed using increasing concentrations of KEDQYMKMTV as substrate. Data were fitted to the Michaelis-Menten equation. C) GLKRNKYLSFHFK is a high-affinity substrate for IRK. Data were collected and analyzed as in B. D) Concentration dependence of KEDQYMKMTV on IRK activity. In vitro kinase reactions with IRK and the IRS-derived peptide substrate included the indicated concentrations of KEDQYMKMTV. Incorporation of [32P] was determined and expressed as percentage inhibition of kinase activity. Data were fitted to a hyperbolic function to estimate Ki. E) Inhibition of insulin-dependent glucose uptake in HepG2 cells by hBVR-based SH2 domain peptides. HepG2 cells were starved, treated with myristoylated peptides and insulin, and assayed for [3H]-deoxyglucose uptake as in Fig. 3.