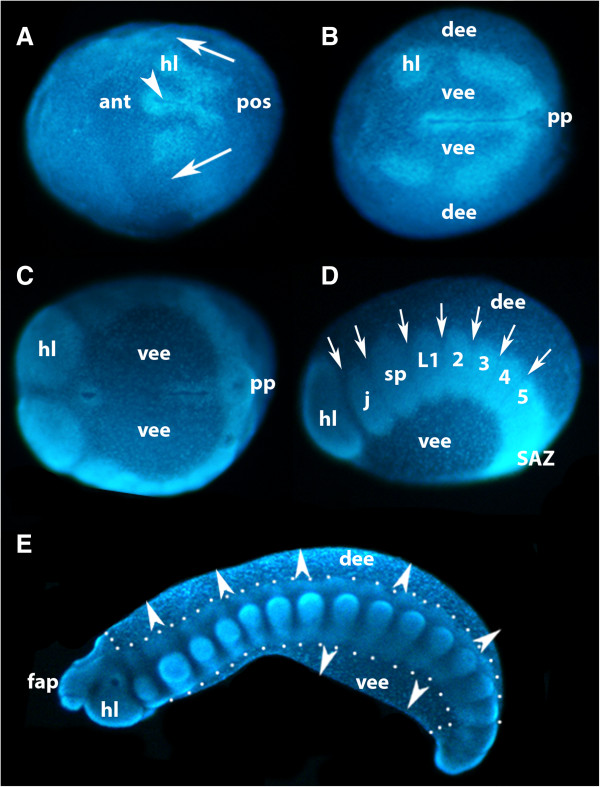
Figure 3.
Formation of the germ band in E. kanangrensis. A germ disc appears after the blastoderm has formed (not shown; [31]), in the centre of which forms a slit-like furrow (arrowhead in A) defining the AP axis. Anterior is to the left. (A) Stage 2 to 3 embryo, ventral view. Cells invaginating at the posterior pole move on either side of the indentation towards anterior (arrows), forming a split germ band. (B) Stage 5 embryo, ventral view. Split germ band subsequently moves towards the anterior and first coelomic pouches bud off from otherwise uniform halves of germ band. The distance between the furrow and the halves of the germ band has increased and ventral extraembryonic ectoderm covers the area between furrow and germ band on either side of the furrow; dorsal to the halves of the germ band is dorsal extraembryonic ectoderm. (C) Stage 8 embryo, ventral view. At later stages, the anterior extent of the split germ band (future head lobes) meets and fuses anterior to the anterior pole of the furrow. (D) Embryo of C, lateral view; dorsal is up. Coelomic pouches are recognizable by areas of higher cell density. As with short germ arthropods, anterior segments represent older (more developed) segments. In the posterior part of the split germ band (anterior to SAZ), coelomic pouches have not yet segregated from newly formed tissue. (E) Stage 15 embryo, lateral view; outline of embryo proper marked by dots. Dorsal and ventral embryonic tissue begins to grow out (arrowheads). 2 to 5, second to fifth walking-limb-bearing segment; ant, anterior; AP, anterior-posterior; dee, dorsal extraembryonic ectoderm; fap, frontal appendage; hl, head lobe; j, jaw; L1, first walking-limb-bearing segment; pos, posterior; pp, posterior pit region; SAZ, segment addition zone; sp, slime papilla; vee, ventral extraembryonic ectoderm.