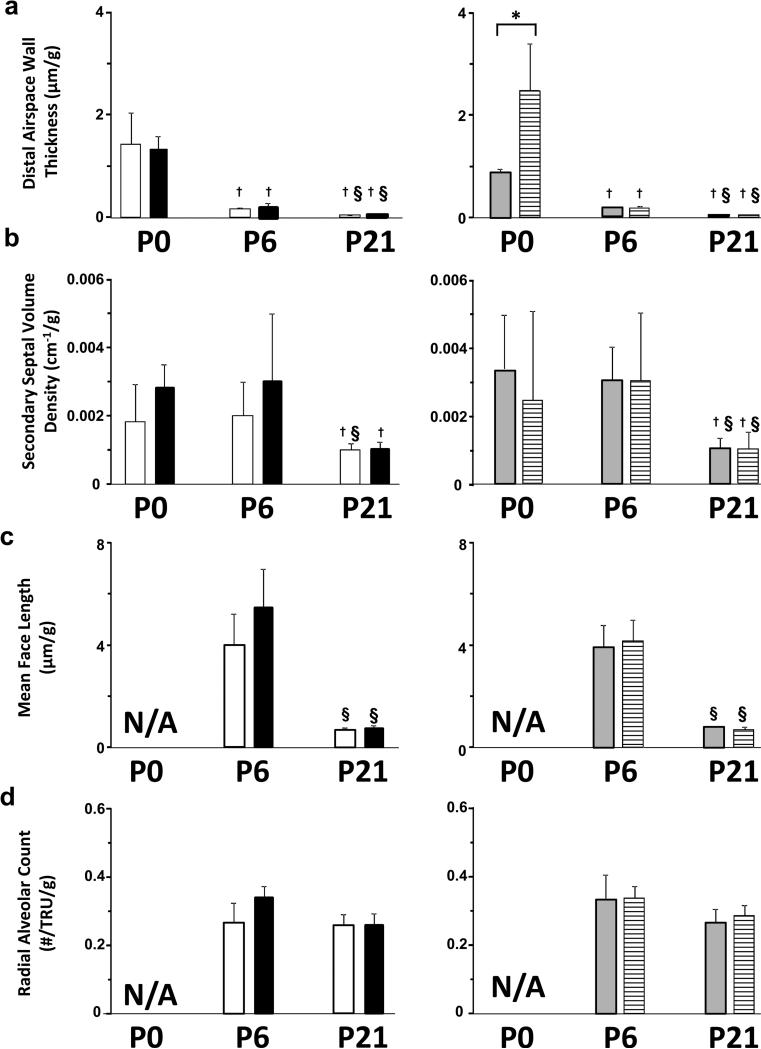
Figure 3.
Effect of IUGR on morphometric parameters of rat lung parenchyma. Results are shown as mean ± SD for n=6/group. White fill indicates male control, black fill indicated male IUGR, grey fill indicates female control and hatched fill indicates female IUGR. Panel a: distal airspace wall thickness for male pups, left side and female pups, right side. Panel b: secondary septal volume density for male pups, left side and female pups, right side. Panel c : mean face length for male pups, left side and female pups, right side. Panel d: radial alveolar count for male pups, left side and female pups, right side. IUGR female pups had significantly thicker distal airspace walls/g body weight at P0 (*p<0.05) than control female pups at P0 (panel a, right side). This difference did not persist at P6 or P21. Secondary septal volume density/g, mean face length/g, and radial alveolar count/g were not affected by IUGR in either male or female pups at any of the endpoints. N/A, not applicable because the lung at P0 is at the saccular stage of lung development. †Different from P0 (p<0.05). § Different from P6 (p<0.05).