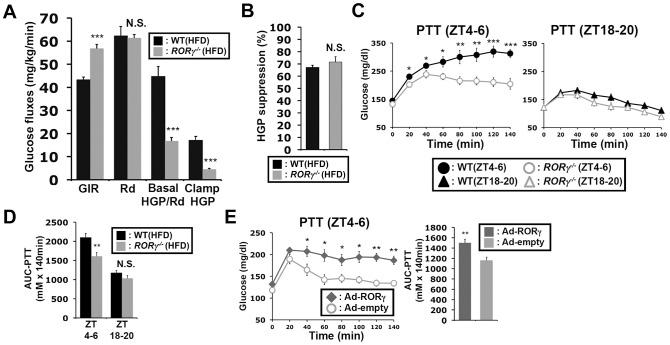
Figure 2. Loss of RORγ leads to reduced hepatic gluconeogenesis at daytime.
(A) The hyperinsulinemic-euglycemic clamp test was performed during daytime (ZT2–9) in WT(HFD) and RORγ−/−(HFD) mice and the glucose infusion rate (GIR), whole-body glucose disappearance (Rd), basal endogenous hepatic glucose production (Basal HGP), and endogenous hepatic glucose production during the clamp (Clamp HGP) were determined. (B) Suppression rate of hepatic glucose production by insulin in WT(HFD) and RORγ−/−(HFD) mice. (C) PTT was examined at ZT4–6 and ZT18–20 in WT(HFD) and RORγ−/−(HFD) mice (n = 8) as indicated. (D) Comparison of AUC for PTT by one way ANOVA. AUC for PTT was also evaluated by 2-way ANOVA: Time period, P = 0.0001; Genotype, P = 0.0009 (not shown). (E) PTT was examined at ZT4–6 in RORγ−/−(HFD) mice injected with either empty or RORγ-containing adenovirus injection (n = 6). Data represent mean ±SEM, * P<0.05, ** P<0.01, *** P<0.001 by ANOVA.