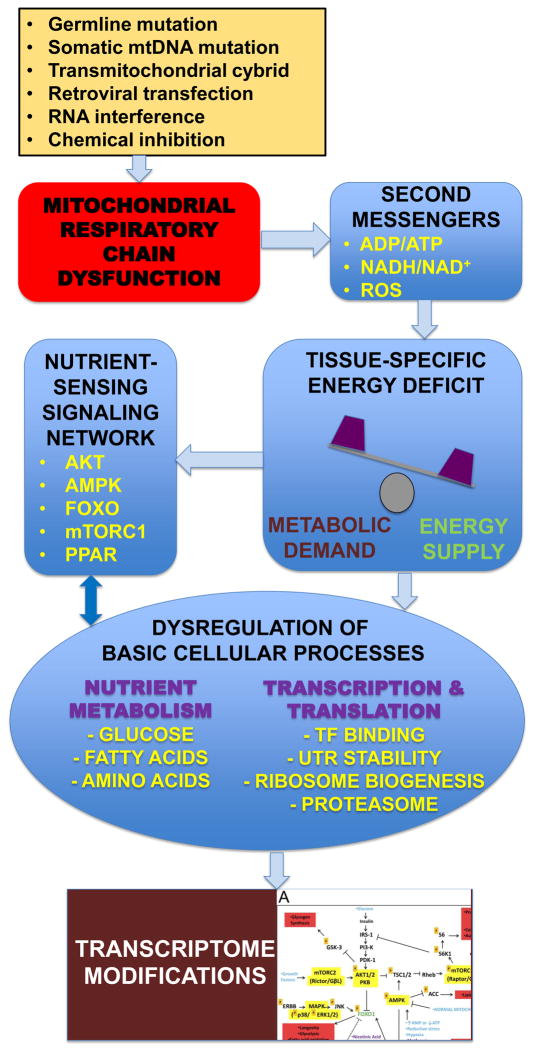
Figure 2. Schematic overview of how central signaling mediators regulate physiologic cellular effects of primary mitochondrial RC dysfunction.
Primary RC dysfunction can result from genetic mutation and/or environmental induction. Impaired mitochondrial RC function causes energy imbalance and triggers a cellular response that is both tissue-specific and nutrient-dependent. Basic cellular processes including nutrient metabolism, transcription, and protein translation are significantly disrupted, likely through modulation of the integrated NSSN. The overall cellular response to mitochondrial RC dysfunction can be partially characterized by transcriptome profiling.