Figure 3. Graphical models for Discretized Sequentially Markov Coalescent (DSMC) models.
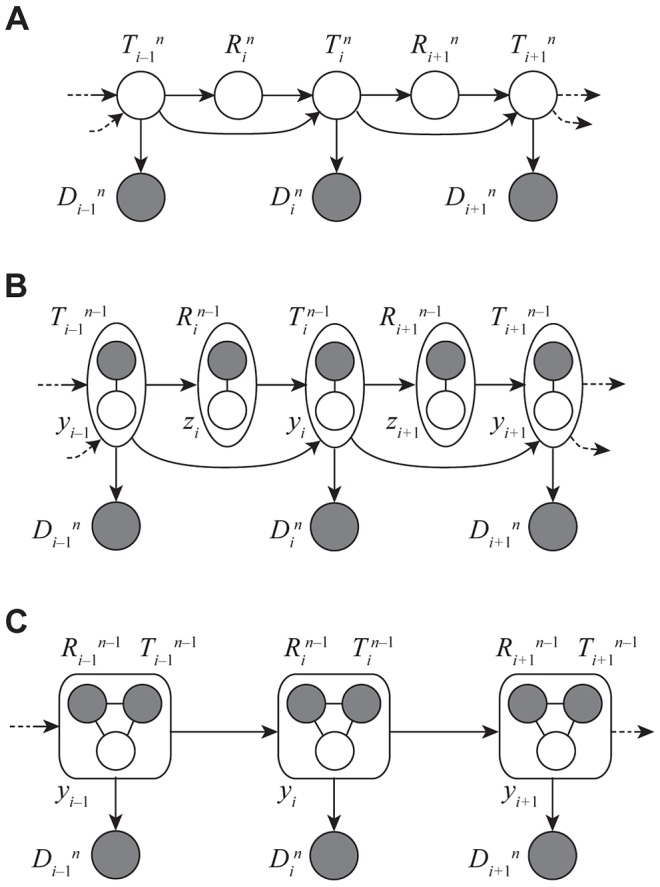
(A) Full DSMC model for  samples with local trees,
samples with local trees, 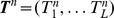 , recombinations,
, recombinations, 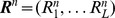 , and alignment columns,
, and alignment columns,  . Together,
. Together, 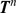 and
and 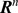 define an ancestral recombination graph,
define an ancestral recombination graph, 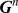 . Solid circles indicate observed variables and empty circles indicate latent variables. Arrows indicate direct dependencies between variables and correspond to conditional probability distributions described in the text. Notice that the
. Solid circles indicate observed variables and empty circles indicate latent variables. Arrows indicate direct dependencies between variables and correspond to conditional probability distributions described in the text. Notice that the 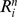 variables can be integrated out of this model, leading to the conventional graph topology for a hidden Markov model. (B) The same model as in (A), but now partitioning the latent variables into components that describe the history of the first
variables can be integrated out of this model, leading to the conventional graph topology for a hidden Markov model. (B) The same model as in (A), but now partitioning the latent variables into components that describe the history of the first  sequences (
sequences (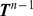 and
and 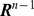 ) and components specific to the
) and components specific to the  th sequence (
th sequence (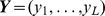 and
and 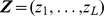 ). The
). The 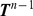 and
and 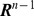 variables are represented by solid circles because they are now “clamped” at specific values. A sample of
variables are represented by solid circles because they are now “clamped” at specific values. A sample of 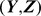 represents a threading of the
represents a threading of the  th sequence through the ARG. (C) Reduced model after elimination of
th sequence through the ARG. (C) Reduced model after elimination of 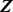 by integration, enabling efficient sampling of coalescent threadings
by integration, enabling efficient sampling of coalescent threadings 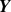 . This is the model used by the first step in our two-step sampling approach. In the second step, the
. This is the model used by the first step in our two-step sampling approach. In the second step, the 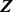 variables are sampled conditional on
variables are sampled conditional on 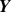 , separately for each
, separately for each 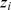 . In this model, the grouped nodes have complex joint dependencies, leading to a heterogeneous state space and normalization structure, but the linear conditional independence structure of an HMM is retained.
. In this model, the grouped nodes have complex joint dependencies, leading to a heterogeneous state space and normalization structure, but the linear conditional independence structure of an HMM is retained.
