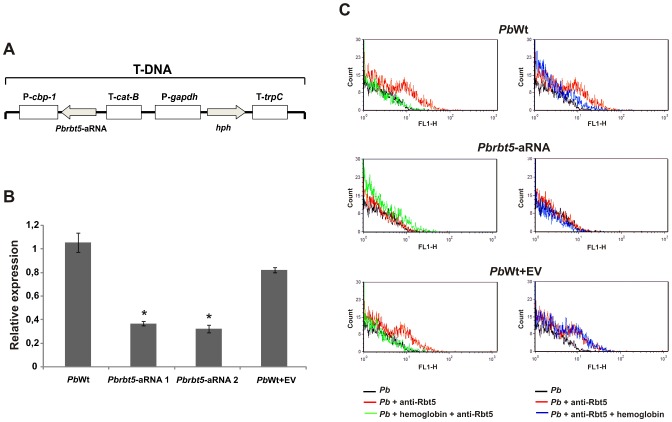
Figure 8. Paracoccidioides Rbt5 knock down via an antisense-RNA (aRNA) strategy.
A. Schematic representation of the T-DNA cassette that was used in this work to perform the Agrobacterium tumefaciens-mediated transformation (ATMT) of Pb339 (PbWt). Pbrbt5-aRNA was cloned in the pUR5750 binary vector under the control of the Histoplasma capsulatum cbp-1 gene promoter region (P-cbp-1) and the Aspergillus fumigatus cat-B gene termination region (T-cat-B). The selection marker that was used in this work was the Escherichia coli hygromycin-resistance gene hph. In the cassette, this gene is flanked by the glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenase promoter region (P-gapdh) and by the trpC termination region (T-trpC) from Aspergillus nidulans. B. After the selection of mitotic stable isolates, a qRT-PCR was performed to analyze the silencing level of the gene in isolates that were transformed with Pbrbt5-aRNA. As controls, rbt5 transcript level from PbWt and PbWt transformed with the empty vector (PbWt+EV) were also quantified. Alpha tubulin was used as the endogenous control. The data are represented as the means ± SD from triplicate determinations. *: statistically significant data as determined by Student's t-test (p<0.05) in comparison with the data that were obtained from PbWt+EV strain. C. Effect of Pbrbt5 deletion on the interaction of Paracoccidioides with heme-containing molecules. Hemoglobin prevents PbWt and PbWt+EV cells to be recognized by the anti-Rbt5 antibodies. However, Pbrbt5-aRNA cells are poorly recognized by the antibody that was raised against Rbt5, which is a process that was not affected by the previous or subsequent exposure of yeast cells to hemoglobin.