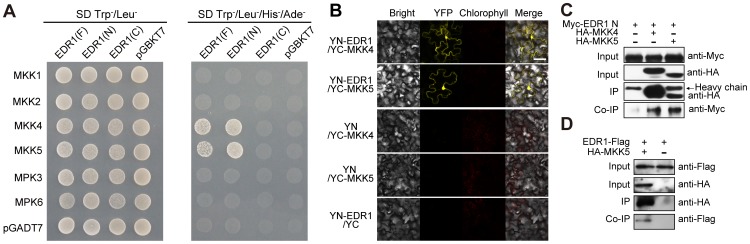
Figure 4. EDR1 interacts with MKK4 and MKK5.
(A) EDR1 full length (F), EDR1 N-terminal domain (N) and EDR1 C-terminal domain (C) were fused to the Gal4 DNA binding domain (BD). MKK1, MKK2, MKK4, MKK5, MPK3 and MPK6 were fused to the Gal4 transactivation domain (AD). Different pairs of constructs were cotransformed into yeast isolate AH109 to test the interaction. 10 µL suspension (OD600 = 0.5) of each cotransformant was dropped on the synthetic dropout (SD) medium lacking Leu and Trp (left) and SD medium lacking Ade, His, Leu and Trp (right), respectively. Pictures were taken after 2 days incubation. (B) YFPYN-fused EDR1 and YFPYC-fused MKK4/MKK5 were co-expressed in N. benthamiana. YFP fluorescence was detected by confocal microscopy. Cotransformants of YFPYN-EDR1 and YFPYC, YFPYN and YFPYC-MKK4, or YFPYN and YFPYC-MKK5 were used as controls. Bar = 50 µm. (C) EDR1 N-terminal domain was expressed alone or co-expressed with MKK4 and MKK5 in N. benthamiana. Proteins were extracted after 48 h, and subjected to immunoprecipitation by anti-HA antibody, followed by immunoblotting using anti-Myc and anti-HA antibodies, respectively. (D) EDR1-Flag transgenic plants and EDR1-Flag/HA-MKK5 double transgenic plants were used for co-IP. The proteins were analyzed by immunoblotting using anti-Flag or anti-HA antibody, respectively. The above experiments were repeated three times with similar results.