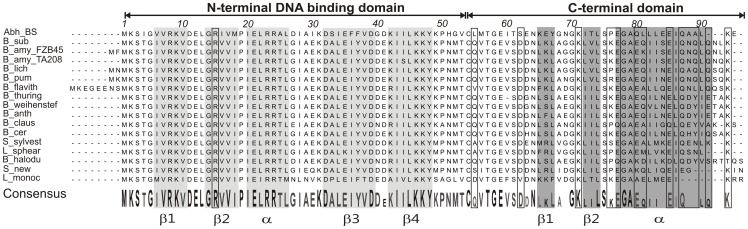
Figure 1. Amino acid alignment of AbrB-like proteins of Bacillus related species.
N- and C-terminal domains are indicated on the top. Known conserved structures of the DNA-binding domain (β1-4 and α) are highlighted in gray according to (7). The structured regions (β1-2 and α) of the C-terminal domain of AbrB from B. subtilis are highlighted in dark gray according to Olson et al. [28]. Amino acid residues that were subjected to the substitution are framed. The consensus sequence resulting from this alignment is given on the bottom and the sizes of the amino acid code indicate the percentage of the similarity (100%, 77%, 65% and 42%). Abh_BS = Abh protein of B. subtilis 168, B_sub = B. subtilis 168, B_amy_FZB45 = B. amyloliquefaciens FZB45, B_amy_TA208 = B. amyloliquefaciens TA208, B_lich = B. licheniformis ATCC14580, B_pum = B. pumilus SARF-032, A_flavith = Anoxybacillus flavithermus WK1, B_thuring = B. thuringensis Al Hakam, B_weihenstef = B. weihenstefanansis KBAB4, B_anth = B. anthracis A0248, B_claus = B. clausii KSM-K16, B_cer = B. cereus ATCC14579, S_silvest = Solibacillus silvestris StLB046, L_shearic = Lysinibacillus sphearicus C3-41, B_halodu = B. halodurans C-125, S_new = Sporosarcina newyorkensis 2681, L_monoc = Listeria monocytogenes L312