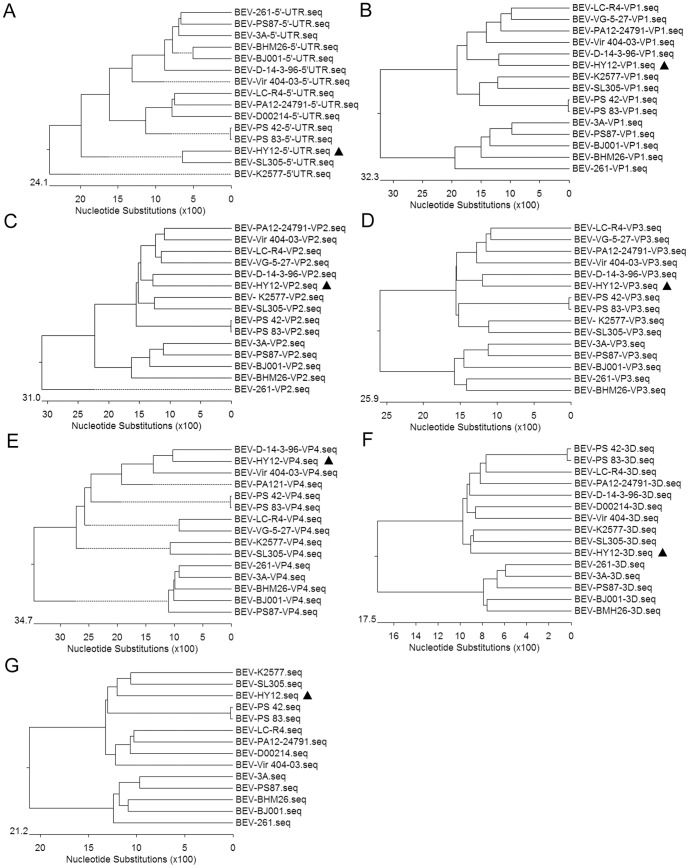
Figure 3. Phylogenetic analysis clustered HY12 strain to a new serotype/genotype within enterovirus E.
Phylogenetic tree were generated by neighbor-joining methods by comparing the sequence regions of 5′-UTR, VP1, VP2, VP3, VP4, 3D, and the complete genome sequences for 15 enteroviruses. HY12 strain was placed to the cluster of enteroviruses E after phylogenetic analysis with the all nucleotide sequence regions except 5′-UTR (B–F). The HY12 strain was revealed as a new serotype/genotype (serotype/genotype 3) that only consists of D14/3/96 and HY12 strains in relation to serotype 1 (LC-R4, VG5-27,Vir 404/03) and serotype 2 (SL305, K2577,PS 42, PS 83) enterovirus strains (B–E). When nucleotide sequences for the non-structural proteins 3D and the complete genome sequence were employed, the HY12 were clustered to the same clade most close to SL305 and K2577 within enteroviruses E (F). However, HY12 strain was clustered to neither clade in enteroviruses E nor enterovirus F using the 5′-UTR sequence (A), suggesting an intraserotypic recombination during HY12 evolution. The position of HY12 was highlighted with a triangle.