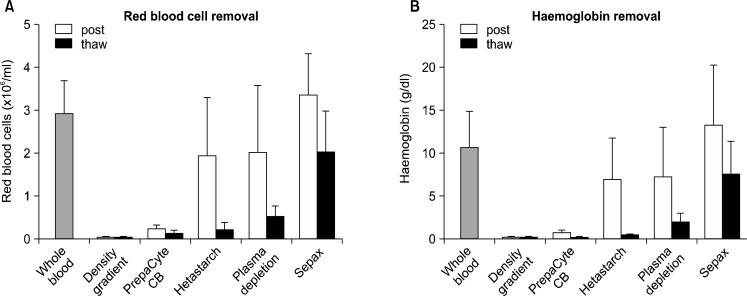
Fig. 4.
Density gradient separation is the most effective method for volume reduction by removal of either; (A) Red blood cells and (B) Haemoglobin. (A) Compared to whole blood, which has an average of 2.9×106 cell/ml (SD±0.75), post processing, density gradient is the most effective method for the removal of red blood cells, it leaves 0.03×106 cell/ml (SD±0.02), PrepaCyte-CB leaves 0.24×106 cell/ml (SD±0.08), Hetastarch leaves 1.93×106 cell/ml (SD±0.22), plasma depletion leaves 2.01×106 cell/ml (SD±1.53) and Sepax leaves 3.33×106 cell/ml (SD±0.95), all results are significant (p=<0.05). Post thaw density gradient is again the most effective method for the removal of red blood cells, it leaves 0.02×106 cell/ml (SD±0.01), PrepaCyte-CB leaves 0.11×106 cell/ml (SD±0.10), Hetastarch leaves 0.22×106 cell/ml (SD±0.16), plasma depletion leaves 0.54×106 cell/ml (SD±0.22) and Sepax leaves 2.01×106 cell/ml (SD±0.94), all results are significant (p=<0.05). (B) Compared to whole blood, which has an average of 10.58 g/dl (SD±4.11), post processing, density gradient is the most effective method for the removal of haemoglobin, it leaves 0.17 g/dl (SD±0.12), PrepaCyte-CB leaves 0.68 g/dl (SD±0.31), Hetastarch leaves 6.94 g/dl (SD±4.74), plasma depletion leaves 7.23 g/dl (SD±5.56) and Sepax leaves 13.07 g/dl (SD±7.03), all results are significant (p=<0.05). Post thaw PrepaCyte-CB is the most effective method for the removal of haemoglobin, it leaves 0.10 g/dl (SD±0.04), density gradient leaves 0.13 g/dl (SD±0.05), Hetastarch leaves 0.46 g/dl (SD±0.29), plasma depletion leaves 1.94 g/dl (SD±1.05) and Sepax leaves 7.57 g/dl (SD±3.70), all results are significant (p=<0.05).