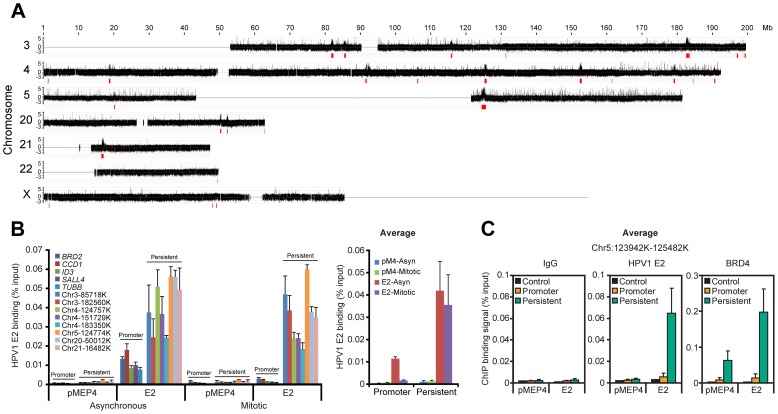
Figure 1. HPV1 E2 binds to broad regions of mitotic chromatin.
A. ChIP-chip binding profile of E2 on a subset of human chromosomes. E2-bound mitotic chromatin was hybridized to microarray chips containing the chromosomes shown. The Y-axis is a scaled log2-ratio of bound to input signal. Large chromatin regions enriched for E2 binding were identified as described in Methods. They are indicated in red underneath the signal map and in Table S2. Chromosomes 18 and 19 were also analyzed but showed no binding peaks and are not shown. B. E2 binding to the large peaks persists throughout the cell cycle. Chromatin was isolated from asynchronous and mitotic fractions from C-33 cells containing empty vector (pMEP4 or pM4) or C-33-1E2 cells (E2) and analyzed by ChIP and Q-PCR using primers (Table S9) for broad E2 binding regions (persistent: throughout the cell cycle) or promoter regions previously shown to bind E2/BRD4 (only in interphase) [34]. Average E2 binding levels were calculated from two independent experiments for five promoter regions and eight broad E2 binding regions. C. Average BRD4 and E2 binding levels on mitotic chromatin to five sites within a broad E2 binding region, chr5:123,942,100–125,482,100 in the absence (pMEP4 empty vector) or presence (E2) of E2 expression. E2 and BRD4 binding was analyzed by ChIP using Q-PCR with the primers described in Table S9 and Figure S1C. Average E2 and BRD4 binding levels and STDEV are presented as calculated from four promoter regions (BRD2, CCD1, SALL4, TUBB) and five binding sites within a broad E2 binding peak in Chr5 (See Figure S1 for complete data).