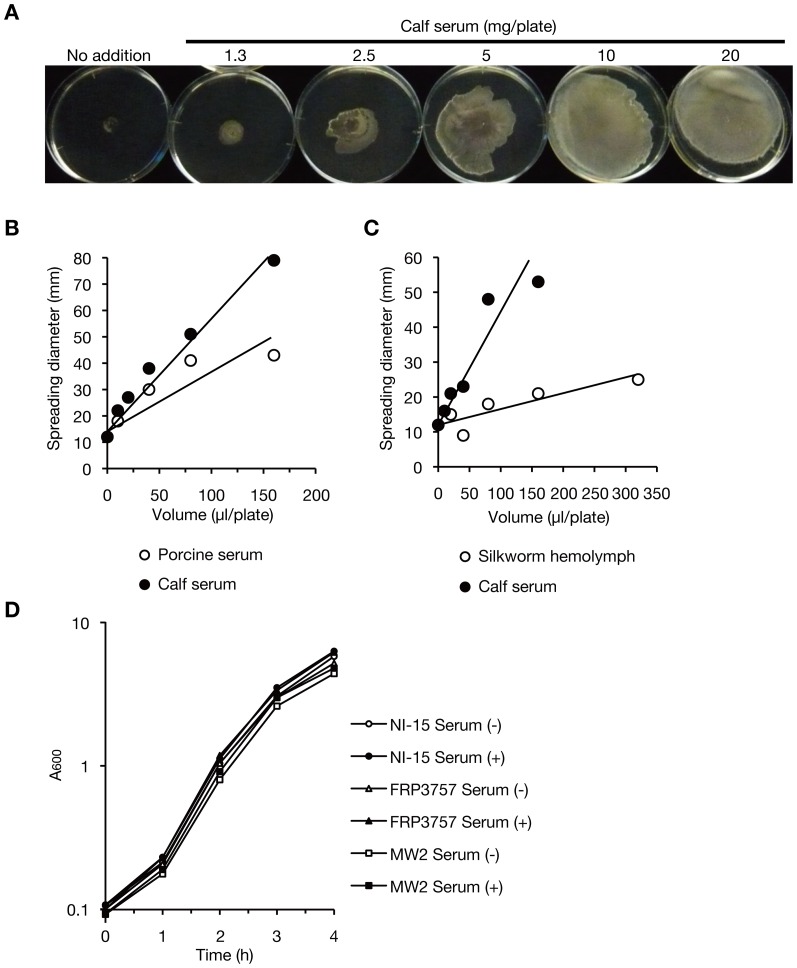
Figure 1. Mammalian serum stimulates S. aureus colony-spreading activity.
(A) Stimulation of colony-spreading activity by calf serum. Overnight culture of S. aureus MRSA NI-15 was spotted on soft agar supplemented with serially diluted calf serum and incubated for 8 h at 37°C. Each plate contained 20 ml soft agar medium. (B) Stimulation of colony-spreading by porcine serum. Porcine serum or calf serum was serially diluted 2-fold and applied to 20 ml soft agar medium and its colony-spreading stimulatory activity was measured. Open circles indicate the halo diameters of giant colonies supplemented with porcine serum and filled circles indicate those supplemented with calf serum. Horizontal axis represents the volume of serum added to 20 ml soft agar medium in a plate. (C) Stimulation of colony-spreading activity by silkworm hemolymph. Hemolymph was collected from fifth instar larvae of silkworms and applied to the soft agar plates in 2-fold serial dilutions and its colony-spreading stimulatory activity was measured. Open circles indicate the halo diameters of giant colonies supplemented with silkworm hemolymph and filled circles indicate those supplemented with calf serum. (D) Growth curves of MRSA NI-15, MW2, or FRP3757 in tryptic soy broth supplemented with or without 1.25% (v/v) calf serum.