Figure 7.
Miniature Neurotransmission Acts Locally to Regulate Bouton Development
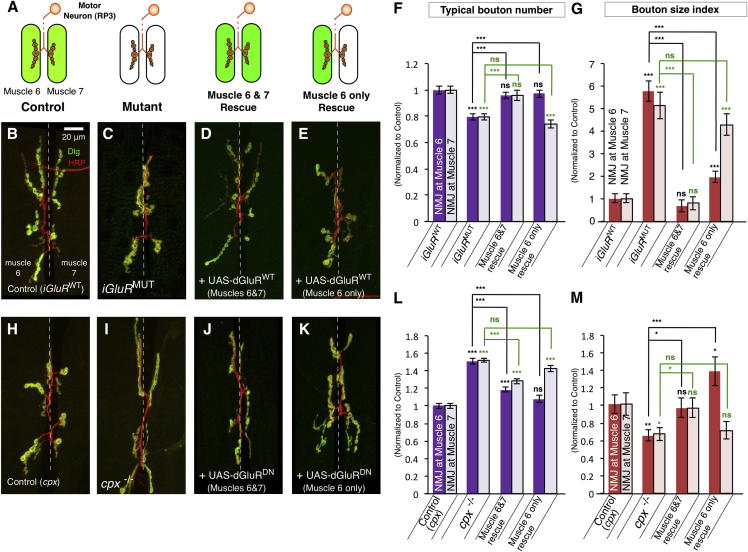
(A) Schematic of the two separate synaptic terminals on muscles 6 and 7 generated by the single motor neuron RP3. Muscle Gal4 lines allow rescue of mutants at either both terminals at muscles 6 and 7 or the terminal at muscle 6 only.
(B–E and H–K) Representative NMJ terminals at muscles 6 and 7, segment A3, labeled with Dlg (green) and HRP (red) from (B) iGluRWT, (C) iGluRMUT, (D) iGluRMUT + UAS-dGluRWT (muscles 6 and 7) (dglurIIAHypo/−,IIBDf/−;C57-Gal4/genomic-dglurIIAE783A,UAS-dglurIIAWT), (E) iGluRMUT + UAS-dGluRWT (muscle 6 only) (dglurIIAHypo/−,IIBDf/−;H94-Gal4,nSyb-Gal80/genomic-dglurIIAE783A,UAS-dglurIIAWT), (H) control(cpx) (cpxDf/+), (I) cpx−/− mutant, (J) cpx−/− + UAS-dGluRDN (muscles 6 and 7) (G14-Gal4/+;cpxDf/−,UAS-dglurIIAE783A), and (K) cpx−/− + UAS-dGluRDN (muscle 6 only) (cpxDf/−,UAS-dglurIIAE783A,H94-Gal4,nSyb-Gal80).
(F, G, L, and M) Quantification of the typical bouton number (F and L) and bouton size index (G and M) from terminals at muscles 6 and 7 (n ≥ 32). Statistical comparisons are labeled in black for terminal 6 and green for terminal 7.
All quantification data are normalized to control. Scale is the same for all images. Error bars indicate ±SEM. ∗p < 0.05, ∗∗∗p < 0.001. See also Figure S7.