FIGURE 5.
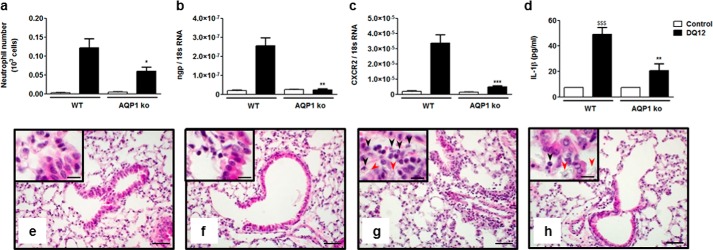
Acute lung inflammatory response to silica particles is reduced in AQP1-deficient mice. a, number of alveolar neutrophils (GR1+ cells) assessed by flow cytometry and expression of the pulmonary neutrophilic markers ngp (b) and CXCR2 (c) quantified by quantitative RT-PCR in WT and AQP1 KO mice 6 h after instillation of silica (DQ12, 2.5 mg) or no instillation (control). d, levels of mature IL-1β in BAL fluid collected 6 h after instillation of silica or no instillation. Data are means ± S.E. n = 3 to 6 animals/condition. e–h, hematoxylin and eosin-stained lung sections obtained from WT (e and g) or AQP1 KO mice (f and h), collected 6 h after instillation of silica (g and h) or no instillation (e and f). Black arrows identify neutrophils, and red arrows identify silica deposition. Scale bars = 50 μm (large panels) and 20 μm (insets). *, p < 0.05; **, p < 0.01; ***, p < 0.001 in silica-treated WT and AQP1 KO mice. p values were calculated by Student Newman-Keuls test.
