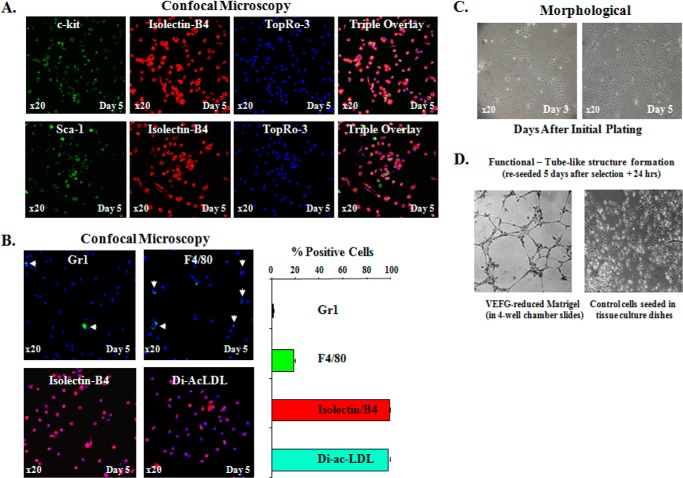
FIGURE 1.
Characterization of bone marrow derived EPCs. A, top row, representative fluorescent confocal images of BM-EPCs triple-stained with c-kit (green, stem/progenitor cell marker), Isolectin-B4 (red, endothelial cell marker), and TopRo-3 (blue, to visualize nuclei) on day 5 after initial plating. Bottom row, representative fluorescent confocal images of BM-EPCs double stained with Sca-1 (green, stem/progenitor cell marker), Isolectin-B4 (red), and TopRo-3 (blue, to visualize nuclei) on day 5 after initial plating. The far right panels in both rows are the triple overlay. These double c-kit/Isolectin-B4 (+) and Sca-1/Isolectin-B4 (+) cells, presumably EPCs, constituted nearly 100% of cells on day 5, respectively, indicating that by this time most if not all of BM-derived cells were identified as EPCs by double (+) staining with EC marker and two progenitor markers (c-kit and Sca-1). B, representative confocal images of BM-EPCs expanded ex vivo for 5 days and stained for hematopoietic lineage markers: Gr1 (to identify neutrophils), F4/80 (to identify macrophages), Isolectin-B4, and the uptake of DiI-ac-LDL while in culture (to confirm EC lineage of the cells). Graphic representation of the percentage (+) cells in BM-EPC cultures for Gr1, F4/80, Isolectin-B4, and DiI-ac-LDL. C, representative phase contrast (×20) images of ex vivo expanded BM-EPC cultures on days 3 and 5 to demonstrate colony-specific expansion of EPCs on day 3 and relative morphologic homogeneity of EPC cultures on days 3 and 5 after initial plating. D, in vitro tube-like structure formation assay on VEGF-reduced Matrigel to confirm EC function of EPCs in BM-derived cultures.