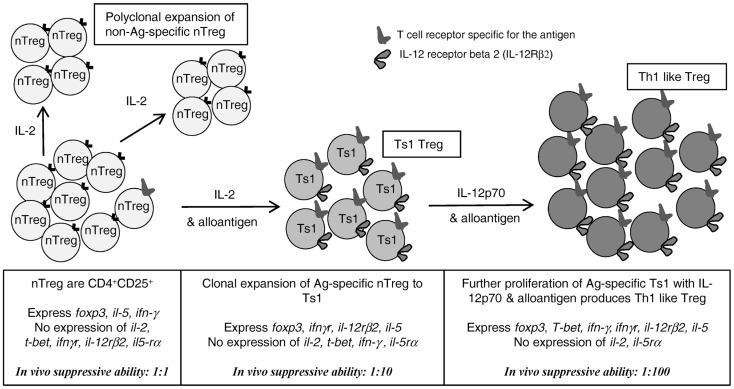
Figure 7.
Proposed pathway for activation/proliferation of alloantigen-specific nTreg and comparison with the non-antigen driven proliferation of nTreg that do not have a TCR specific for the antigen. rIL-2, without antigen, induced proliferation of nTreg, which retain the characteristics of nTreg. In presence of antigen and rIL-2, nTreg with TCR for the stimulating antigen are first induced to express a Ts1 phenotype, including expression of ifngr, il-12rβ2, foxp3, and il-5. Stimulation of these Ts1 cells with alloantigen and rIL-12p70 in the absence of rIL-2, induced Th1-like Treg that retain the Ts1 phenotype, but in addition express t-bet and ifn-γ and no il-2. These have enhanced capacity to suppress in vitro and in vivo at lower ratios to effector CD4+ T cells, than nTreg (1:100 vs. 1:1) and Ts1 [1:100 vs. 1:10 (2)]. Thus, inflammatory Th1 cytokines drive induction of alloantigen-specific Treg; the first step is induction of alloantigen-specific Ts1 cells by the early Th1 cytokine IL-2; the second step is induced by rIL-12p70 only after IL-2 production wanes. rIL-12p70 induces Th1-like Treg that express both t-bet and foxp3 as well as ifn-γ, ifngr, and il-5. Adapted from Figure 1 in Hall et al. (1).