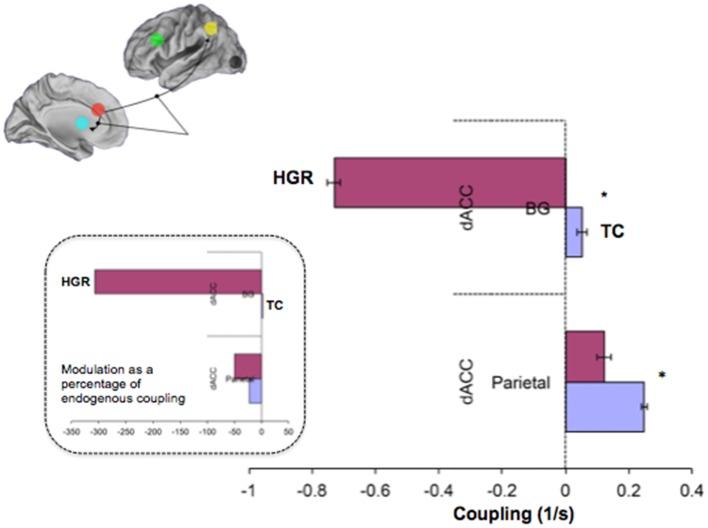
Figure 9.
Contextually modulated connections in the winning model in TC and HGR. Bayesian parameter averages over all subjects for the winning model (Figure 7 reproduced here) are depicted for each modulated connection (± posterior standard errors). The source regions are vertically labeled and the target regions are horizontally labeled. For both dACC efferent pathways, attention has different patterns of modulation in HGR. The degree of positive modulation (excitatory) on the dACC–Parietal pathway is reduced in HGR, suggesting that the gain in connection strength is lower when implementing attention processing. Moreover, the dACC–BG pathway in HGR is significantly inhibited during attention processing. The inset depicts contextual modulation expressed as a percentage of the endogenous coupling values (Figure 8). This turning down may reflect critical sub-network disengagement in HGR during attention processing and may encode particular vulnerability for impaired attention, cognition, and control that has been documented in HGR groups.