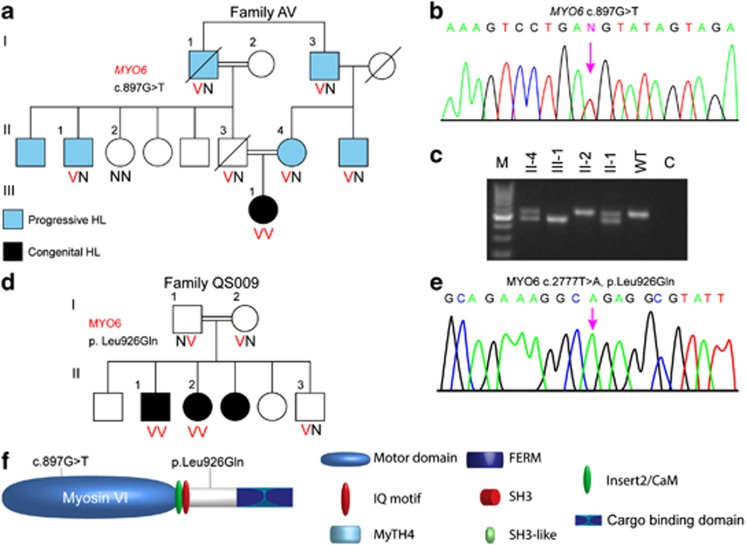
Figure 1.
Analysis of myosin VI mutations. (a) Pedigrees and segregation analysis of Family AV. (b) Partial sequences of MYO6 exon 10 from a normal hearing and affected proband AV-III-1 demonstrating the c.897G>T splicing mutation. (c) cDNA was amplified from blood from the patients of Family AV, using primers from exon 9–12 to generate a 545-bp fragment. Exon 10 was lost in the resultant cDNA of patient AV-III-1, confirmed by sequencing. (d) Pedigrees and segregation analysis of Family QS009. (e) Partial sequences of MYO6 from an affected proband demonstrating the c.2777T>A, p.Leu926Gln, as shown by a chromatogram. (f) Schematic representation of myosin VI shows the location of the potential splicing mutation c.897G>T in the ATPase activity domain in the motor and p.Leu926Gln, located in a potential proximal dimerization region in the tail of the myosin VI protein.