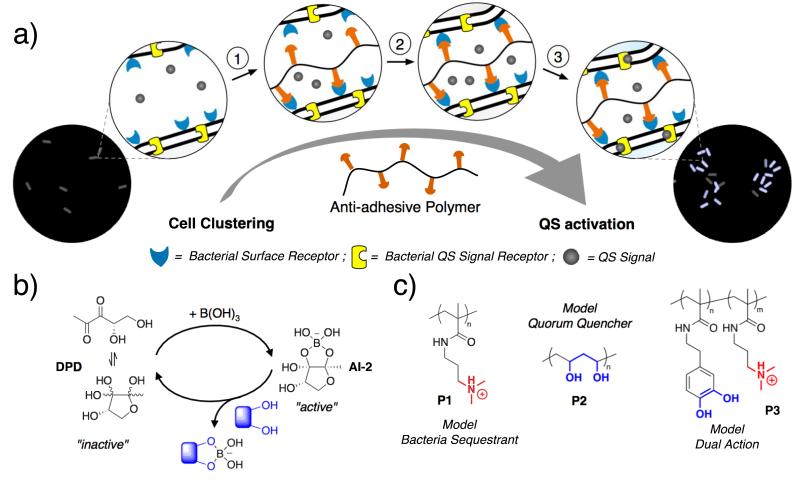
Figure 1. QS induction in the AI-2 network.
a) Schematic representation of QS activation by “bacteria sequestrants” that promote bacteria clustering: ☉ Polymer binds to the surface of the bacteria via multivalent interactions. ◯ Bacteria are cross-linked as polymer interacts with different bacterium. ☽ Signal diffusion is limited maintaining a high concentration within the cell cluster b) Key components of the autoinducer-2 network, including 4,5-dihydroxy-2,3-pentanedione (DPD) and the active species formed in the presence of B(OH)-in the media. Mechanism of AI 2 quenching by competitive binding with diols. c) Structure of the polymers employed in this work: poly(N-[3-(dimethylamino)propyl] methacrylamide) (P1), poly(vinyl alcohol) (P2) and poly(N-dopaminemethacrylamide-co-N-[3-(dimethylamino)propyl] methacrylamide) (P3).