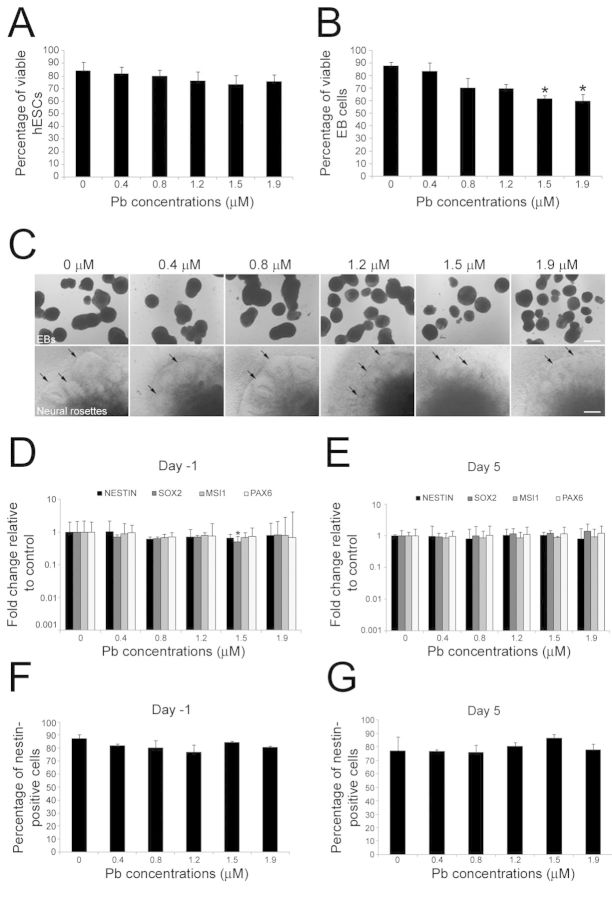
FIG. 3.
Effects of acute exposure to Pb on the neural differentiation of hESCs. (A) and (B): Analysis of cell viability by Trypan blue staining. Undifferentiated (A) and differentiating(B) hESCs were exposed to 0–1.9μM Pb for 24 h (paradigms A and B in Fig. 1A). The percentage of viable cells was calculated as follows: (total number of cells-number of nonviable dark-blue stained cells)/(total number of cells) x 100. Histogram values are means ± SEM. *Statistically significant difference (p < 0.05; n = 3, one-way ANOVA) between Pb-exposed and control hESCs. (C) Formation of embryoid bodies (EBs) and neural rosettes (arrows) from hESCs is not prevented by acute Pb exposure. (D) and (E): Quantitative RT-PCR expression analysis for the NPC marker genes NESTIN, SOX2, MSI1, and PAX6 in hESC-derived cells at day 19 of the differentiation protocol, following 24-h Pb exposure at day -1 (D) or day 5 (E). Histogram values represent means and error bars represent 95% interval confidences. *Statistically significant difference (p < 0.05; n = 3, one-way ANOVA) between Pb-exposed and control hESCs. The percentage of Nestin-positive cells generated from hESCs exposed to Pb either at day -1 (F) or day 5 (G) of the differentiation protocol was not significantly different from control percentages. Histogram values represent means ± SEM (n = 3; one-way ANOVA). Bar: 150 μm.