Figure 1.
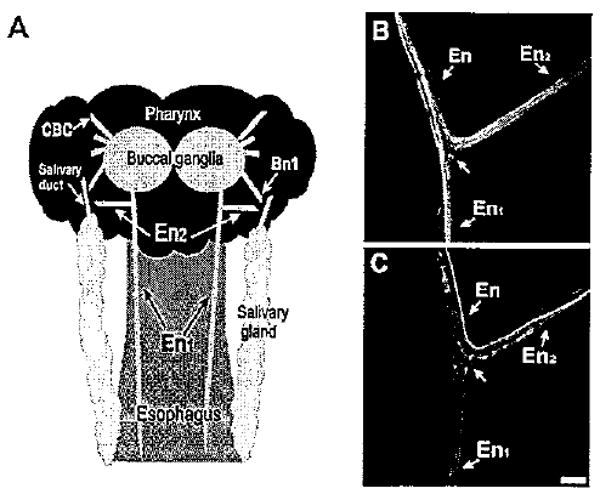
Aminergic fibers in the esophageal nerve. A: Schematic diagram (not drawn to scale) of the structures examined in this study. The posterior region of the buccal mass, to which the paired buccal ganglia adhere, corresponds to the pharynx. One esophageal nerve emerges from each buccal hemiganglion. Near its origin, the esophageal nerve bifurcates into a posterior branch (En1), which projects along the length of the esophagus, and a shorter anterior branch (En2), which projects laterally toward the pharynx and salivary gland. In the region of the salivary duct, the En2 projection converges with buccal nerve 1 (Bn1). CBC, cerebral buccal connective. B: THli in the esophageal nerve. At the En bifurcation, THli fibers could be traced to both the En1 and En2 branches. C: Serotonin-like immunoreactivity in the En. Several 5HTli fibers were observed in each En branch. Scale bar = 100 μm.
