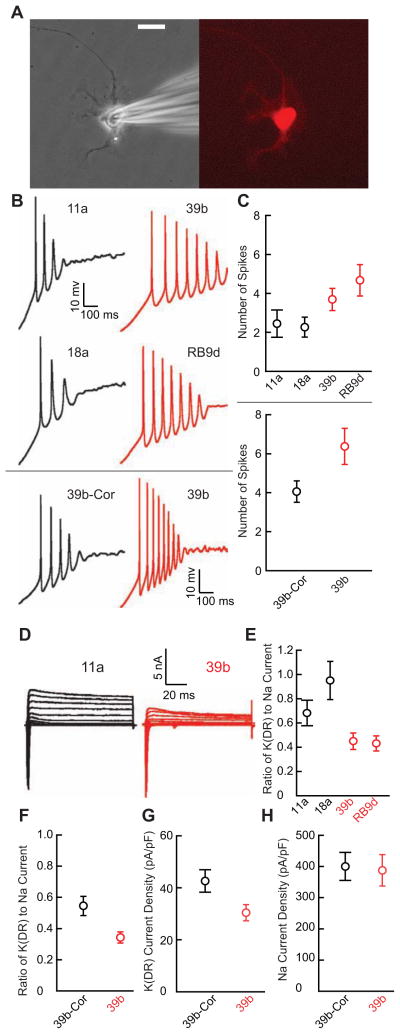
Figure 2. ALS Patient-Derived Motor Neurons are Hyperexcitable and Have Reduced Delayed-Rectifier Potassium Currents Compared to Control-Derived Motor Neurons.
(A) An iPSC-derived motor neuron identified by Hb9::RFP lentiviral transduction (right) and during patch clamp recording (left) after culture for 28 days. Scale bar 20 μm.
(B) Representative current clamp recordings during ramp depolarization from control and ALS patient-derived motor neurons (upper four panels); sample recordings from separate experiments comparing the isogenic correction of the 39b SOD1A4V mutation (39b-Cor) and 39b (lower two panels).
(C) Upper panel: Average number of action potentials elicited by ramp depolarization from control (11a, n=12; 18a, n=11; control mean 2.5 ± 0.4) and ALS (39b, n=13; RB9d, n=12; ALS mean 4.2 ± 0.5) motor neurons obtained from four separate differentiations (p<0.05, Mann-Whitney U test). Lower panel: Separate experiments showing average number of action potentials during ramp depolarization from 39b-Cor (n=17; mean 4.1 ± 0.5) and 39b (n= 19; mean 6.4 ± 0.9) motor neurons from three additional differentiations (p<0.05, Mann-Whitney U test).
(D) Sample voltage clamp recordings from control and ALS-derived Hb9::RFP-positive motor neurons cultured for 28 days.
(E) Average delayed-rectifier (DR) steady-state potassium current amplitude relative to peak sodium current amplitude in control (11a, n=12; 18a, n=11; control mean 0.88 ± 0.087) and ALS (39b, n=13; RB9d, n=12; ALS mean 0.44 ± 0.054) patient-derived motor neurons from four differentiations (p<0.001, t-test).
(F) Experiments from three separate differentiations showing average delayed-rectifier steady-state potassium current amplitude relative to peak sodium current amplitude in 39b-Cor (n=18; mean 0.54 ± 0.061) and 39b (n=19; mean 0.32 ± 0.036; p<0.005, t-test).
(G) Direct measurement of delayed-rectifier voltage-gated potassium current isolated by holding at −30 mV, stepping to a test-potential of +40 mV for 2 s and normalizing steady state current amplitude to cell capacitance in 39b-Cor (n=19; mean 42.6 ± 4.3 pA/pF) and 39b (n=18; mean 30.3 ± 3.1 pA/pF; p<0.05, t-test) derived motor neurons using cells from two additional separate differentiations.
(H) Peak sodium current amplitude normalized to cell capacitance in 39b-Cor (n=16; mean 400.4 ± 44.7 pA/pF) and 39b (n=15; mean 387.1 ± 50.5 pA/pF; p=0.8, t-test) derived motor neurons.