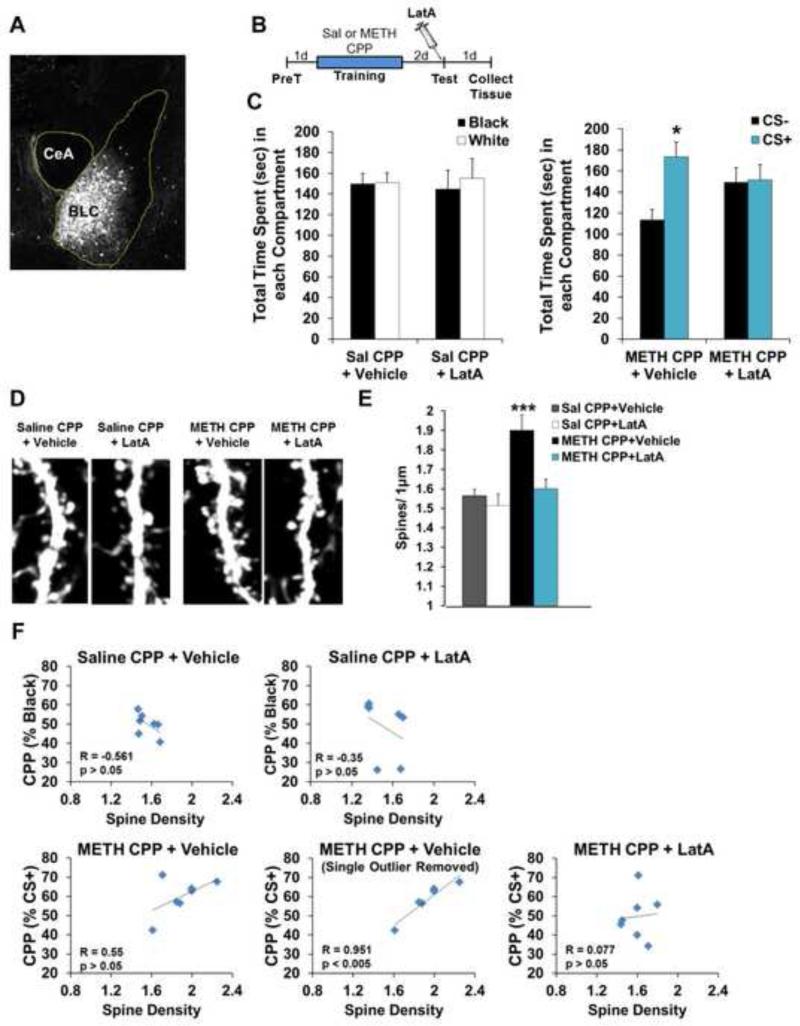
Figure 6.
The spine density increase associated with METH CPP is reversed with memory disruption by F-actin depolymerization. (A) Representative image of eGFP expression in the BLC of Thy1-GFP(m) mice. (B) Schematic of experimental design. (C) Intra-BLC LatA disrupts METH-associated memory in Thy1-GFP(m) mice (right panel), but has no effect on behavior in mice trained with saline on both sides of the CPP apparatus (left panel) (n=7 per group). (D) Representative images of BLC dendritic spines from Thy1-GFP(m) mice after CPP training with saline or METH, followed by intra-BLC vehicle or LatA treatment. (E) METH-associated memory was accompanied by an increase in BLC spine density that was reversed by F-actin depolymerization. (F) Effect of intra-BLC LatA on correlations between memory performance and spine density. Error bars represent SEM.