Figure 2.
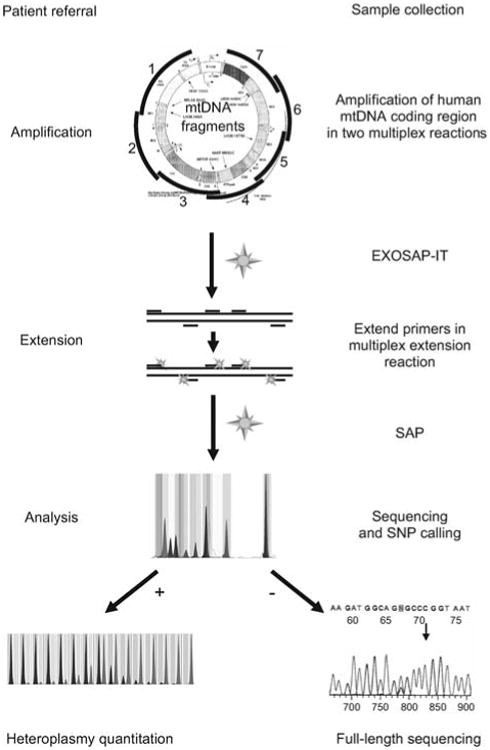
Flow sheet for SNaPshot identification of mtDNA SNVs.
The entire coding region is PCR amplified using multiplex amplification. Amplicons are EXOSAP-treated, mixed with non-overlapping primers designed to end at the base 5′ to the SNV site of interest, and the primers cyclically extended using the four differentially fluorescently labeled dideoxyribonucleotides. The reactions are then treated with shrimp alkaline phosphatase (SAP) and resolved on an ABI 3130×1 capillary. The fluorescent base or bases incorporated into the 3′ end of each primer then reveal the allele present for that SNV. By using multiple non-overlapping primers, multiple SNVs can be interrogated in one reaction. Individual SNV alleles can then be confirmed by quantitative SNaPshot analysis or by direct dideoxyribonucleotide sequencing. Heteroplasmy can be quantified by the relative fluorescence of the mutant and normal bases, compared against a standard curve containing SNV mixtures of known percentages. MITOMAP (Ruiz-Pesini et al., 2007) and MITOMASTER (Brandon et al., 2009) are then used for data interpretation.
