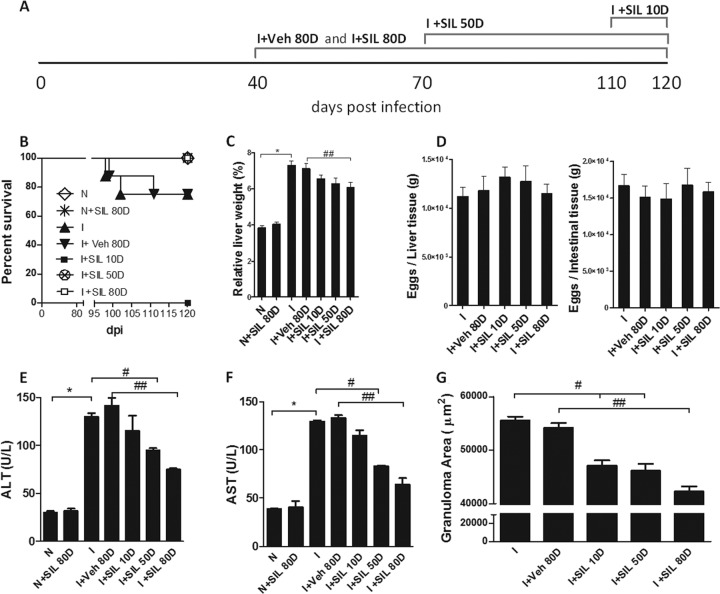
FIG 1.
Silymarin reduced mortality and liver morbidity in chronic S. mansoni infection. Mice were left untreated (I) or treated with carboxymethylcellulose (I+Veh 80D) or silymarin (10 mg kg−1) for 10 days (I+SIL 10D), 50 days (I+SIL 50D), or 80 days (I+SIL 80D). Noninfected groups were used as controls (N and N+SIL 80D). (A) Schematic image describing the experimental design; (B) survival curve; (C) liver weights in relation to total animal weight; (D) equal distribution of tissue eggs; (E) ALT levels in sera; (F) AST levels in sera. (G) Granuloma areas were evaluated on histological sections (5 μm) of hepatic tissue stained with H&E; all granulomas containing a central viable egg were measured. Results are expressed as means + standard errors (SE) (n = 8). *, P < 0.05 for N versus I comparison; #, P < 0.05 for I versus I+SIL 50D and I+SIL 10D; ##, P < 0.05 for I+Veh 80D versus I+SIL 80D. Results are representative of two similar experiments.