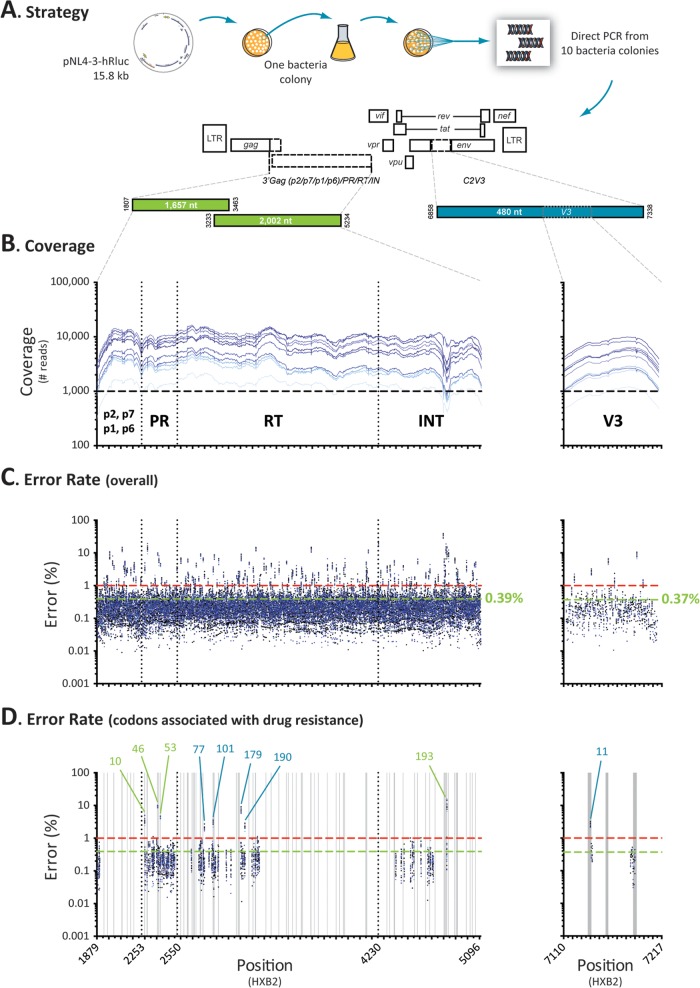
FIG 2.
Error rate determination. (A) The pNL4-3-hRluc plasmid containing the entire genome of the wild-type HIV-1NL4-3 strain (69) was transformed into bacteria and the gag-p2/NCp7/p1/p6/pol-PR/RT/IN and env-C2V3 fragments were PCR amplified and deeply sequenced from 10 individual colonies. The reads from each individual NL4-3 clone were independently mapped to the pNL4-3-hRluc reference sequence (13, 69) using Segminator II (76). (B) Coverage, i.e., number of reads per nucleotide position, for the 10 NL4-3 clones. (C) Overall (point mutation, insertions, and deletions) error rate per nucleotide position calculated using a Phred quality score of 20. The mean error rates for the gag-p2/NCp7/p1/p6/pol-PR/RT/IN and env-V3 regions are indicated in green, while the minimum thresholds to detect mutations in the minority HIV-1 variants with this novel assay (1%) are indicated by dashed red lines. (D) Overall error rate in positions associated with drug resistance. Only codon changes with error rates >1% are indicated, i.e., L10, M46, and F53 in the protease region, F77, K101, V179, and G190 in the RT region, G193 in the integrase region, and amino acid 11 in the V3 region. Homopolymeric regions, defined as four or more identical consecutive nucleotides, are indicated as vertical gray bars.