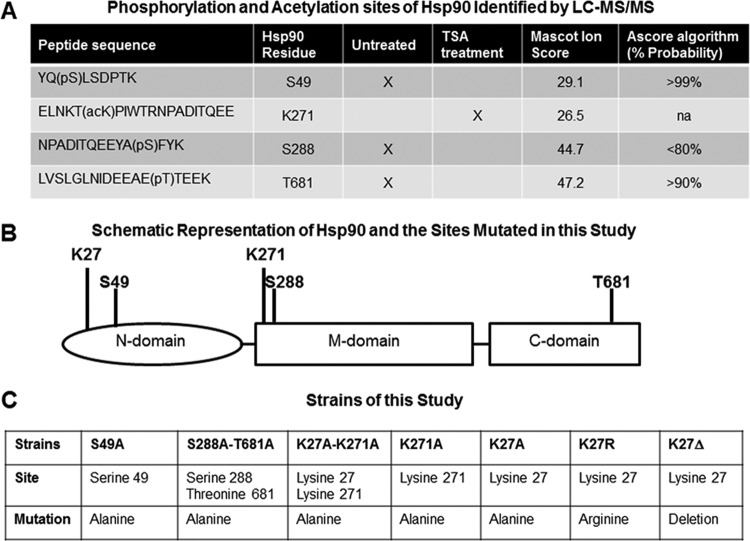
FIG 1.
Mutations of phosphorylation and acetylation sites of Hsp90. (A) Phosphorylation and acetylation sites of Hsp90 identified by TiO2 enrichment and LC-MS/MS analysis. Phosphorylated residues were identified at S49, S288, and T681 in the untreated Hsp90-EGFP strain (standard growth conditions in liquid GMM). Acetylation of K271 was detected after exposure to the lysine deacetylase inhibitor trichostatin A (TSA). Sequences of peptides with phosphorylated serine (pS) and threonine (pT) residues or acetylated lysine (acK) residues are shown in the first column. A Mascot identity score of >41 indicates identity or extensive homology (P < 0.05). The Ascore algorithm indicates the probability of localization of the phosphorylation sites and is not applicable (na) for the acetylation sites. (B) Schematic representation of the A. fumigatus Hsp90 protein with 706 amino acids consisting of the N-terminal, middle (M), and C-terminal domains. Positions of the K27, S49, K271, S288, and T681 amino acid residues that were mutated in this study are shown. (C) Strains generated in this study. Phosphorylation sites of Hsp90 (S49, S288, and T681) identified by LC-MS/MS were mutated to alanines. The K271 site, which was found to be acetylated after treatment with deacetylase inhibitor, was mutated to alanine. The K27 site, which was previously identified as acetylated in yeasts, was further investigated by mutation to either alanine or arginine or deletion.