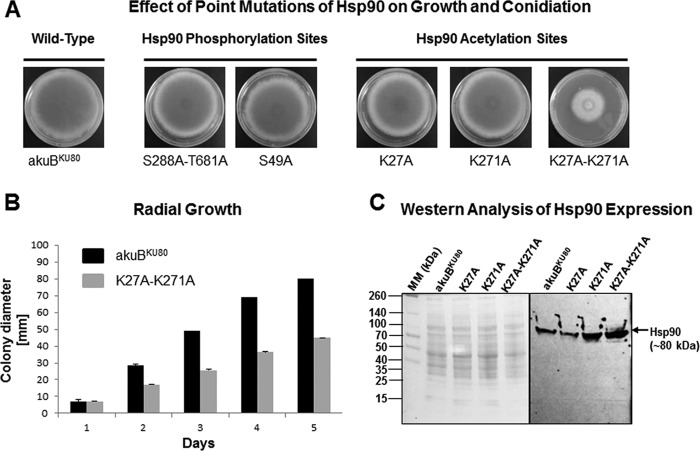
FIG 2.
Phenotypic analyses of mutated Hsp90 strains. (A) Mutations of the phosphorylation sites S49, S288, and T681 to alanines (S49A and S288A-T681A strains) did not result in any growth defect compared to growth of the control akuBKU80 strain. While individual mutation of the lysine sites K27 and K271 to alanines (K27A and K271A strains) did not result in any phenotypic alteration under standard growth conditions, the double mutation (K27A-K271A strain) induced a substantial growth and conidiation defect. Pictures were taken after 5 days of growth on GMM agar at 37°C. (B) Radial growth of the K27A-K271A strain was assessed by daily measurement of the colony diameter compared to that of the akuBKU80 strain over 5 days (GMM agar at 37°C). A significant growth defect was apparent from day 2. On day 5, radial growth of the K27A-K271A strain was decreased by 44% (P < 0.0001). (C) Western analysis using anti-Hsp90 antibody showed that expression of the Hsp90 protein was stable in the different lysine mutant strains, K27A, K271A and K27A-K271A, compared to the akuBKU80 strain, as demonstrated by the detection of a band of approximately 80 kDa (corresponding to Hsp90) in all of them (right panel). Fifty micrograms of total protein from each strain was used, as shown by the similar patterns of Ponceau S protein staining of the PVDF membrane (left panel). MM, molecular mass.