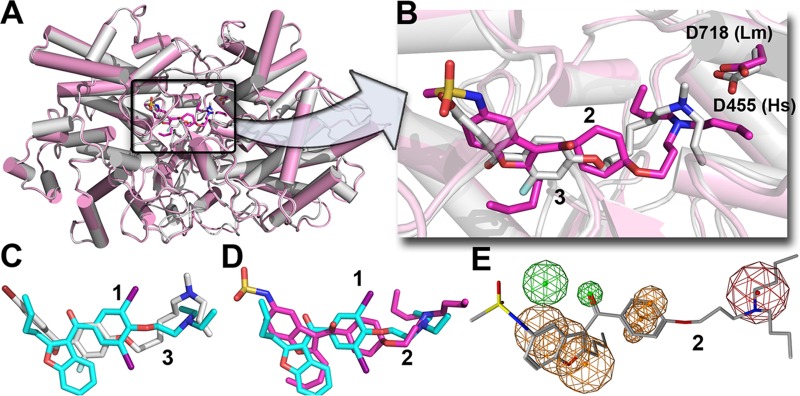
FIG 8.
Suggested binding site for dronedarone in L. mexicana oxidosqualene cyclase. (A) Glide docking pose of dronedarone (compound 2) bound to a Phyre2-predicted structure model (magenta) superimposed on the X-ray structure of Ro-48-8071 (compound 3, white) bound to human OSC (PDB code 1W6J). (B) Expanded view of panel A, showing the most highly conserved Asp residues in the catalytic site. Dronedarone is in magenta, and Ro-48-8071 (compound 3) is in white. The cationic centers likely interact with the conserved Asp. (C) Superimposed structures of Ro-48-8071 (compound 3) bound to HsOSC and amiodarone (compound 1) docked to the T. cruzi OSC model. (D) Comparison between dronedarone (compound 2) and amiodarone (compound 1) docked poses. (E) Common feature pharmacophore for potent HsOSC inhibitors (compounds 3 to 7) superimposed on dronedarone (compound 2) showing common cationic (red) and aromatic/hydrophobic (orange) features.