Figure 2.
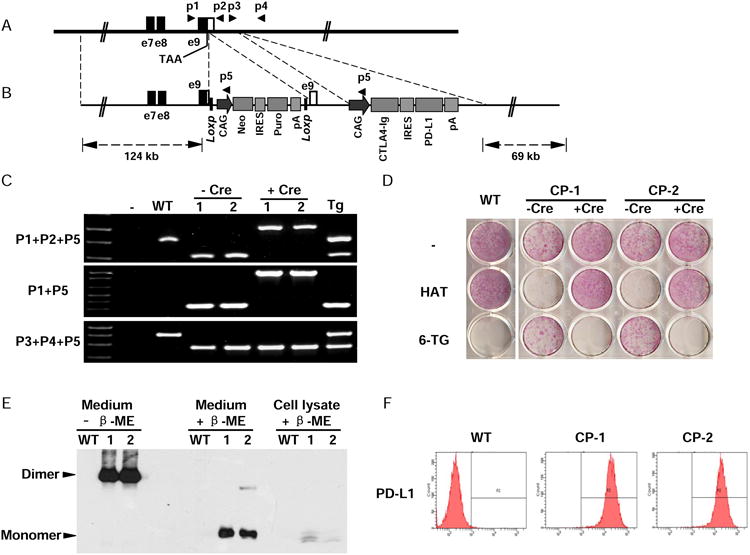
Generation of Hues 3 CP hESCs. (A) The endogenous human hypoxanthine phosphoribosyltransferase 1 (HPRT1) locus. Open box indicates the 3′ UTR of HPRT1. Filled boxes indicate part of HPRT1 coding sequence. The stop codon (TAA) and the binding sites of the primers used for identification of targeting clones are indicated. (B) BAC-based targeting vector. The LoxP flanked selection cassette was inserted between the stop codon and the PolyA signal sequence of HPRT1 to block its expression, introducing both positive and negative selections during targeting process. The CAG promoter-driving expression cassette, CAG/CTLA4-Ig/IRES/PD-L1/pA, was inserted about 600 bps downstream of HPRT1 gene. The sizes of homologous arms are indicated. IRES, internal ribosomal entry site. (C) PCR analysis of the targeted clones in human male ESCs (HUES 3). WT, wide type parental HUES 3; 1 & 2, two targeted clones CP-1 & CP-2; Tg, a random integration clone. The primers used are indicated in A and B. (D) Drug sensitivity assay to confirm the expression and function of HPRT1 in the knock-in clones. Cells were seeded onto 12-well plates. At the following day, the media were changed to that containing hypoxanthine/aminopterin/thymidine (HAT), or 6-thioguanine (6-TG), or without a drug. After being treated for three days, the cells were stained with an alkaline phosphatase detection kit. (E) The expression and secretion of CTLA4-Ig was confirmed. Loading buffer with or without the reducing agent β-mercaptoethanol was used to evaluate the dimerization status of CTLA4-Ig. (F) The surface expression of PD-L1 was confirmed by flow cytometry. See also Figure S1
