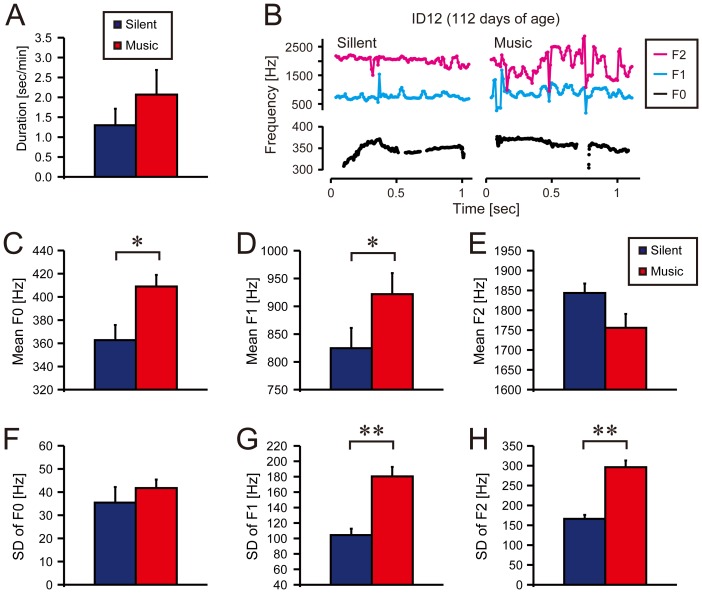
Figure 3. Spontaneous vocalizations of infants during the music condition “Go Trippy” by WANICO feat. Jake Smith (red) and in the silent condition where no auditory stimulus was present (blue).
Error bars indicate standard errors (SE) among the participants. (A) No significant difference was found in mean duration of vocalization per minute between the silent and music conditions (Wilcoxon signed-rank test, Z = 1.62, p = 0.11). (B) Typical time series of fundamental (F0, black lines) and formant frequencies (F1 and F2, cyan and magenta lines, respectively) within utterances. (C, D) Mean F0 and F1 was significantly higher in the music condition than in the silent condition (Z = 2.39, *p<0.05; Z = 2.06, *p<0.05, respectively). (E, F) There were no significant differences in mean F2 and SD of F0 (Z = 1.92, p = 0.06; Z = 1.16, P = 0.25, respectively). (G, H) SD of F1 and F2 were significantly higher in the music condition than in the silent condition (Z = 3.43, **p<0.001; Z = 3.48, **p<0.001, respectively).