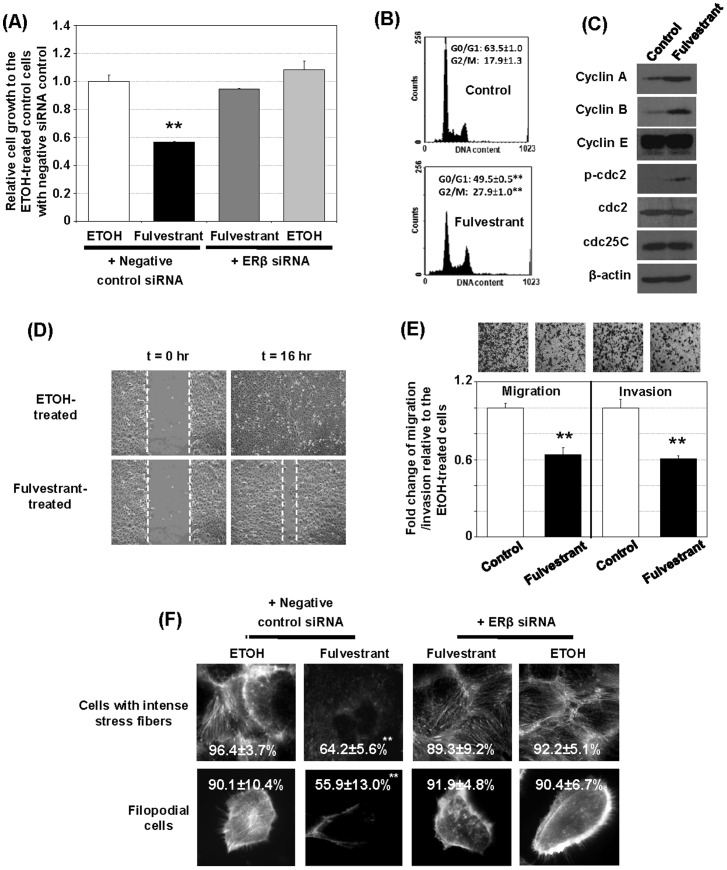
Figure 1. Fulvestrant inhibits DU145 cell growth, migration, and invasion.
(A) Fulvestrant induces growth inhibition of DU145 cells via an ERβ-dependent mechanism. Growth of the fulvestrant-treated DU145 cells with or without ERβ siRNA knockdown for 4 days relative to the ethanol-treated control cells with negative-control siRNA are presented and compared (n = 8). ERβ expression was also knocked down by another siRNA (siRNA#2) and the similar results were obtained (Figure S5). (B) Fulvestrant induces DU145 cell-cycle arrest at G2/M phase. Representative DNA histograms of 48 hrs fulvestrant -or ethanol- (control) treated cells and percentage distributions of the cells at G0/G1 and G2/M phases (n = 3) are presented and compared. (C) Fulvestrant induces expression of G2/M markers. DU145 cells were treated with fulvestrant or ethanol for 2 days (control) and cell cycle markers were determined by Western blot analysis. Two independent experiments were performed and one representative set of data was presented. (D) Fulvestrant suppresses cell migration. A wound-healing assay was performed on the fulvestrant- and ethanol (EtOH)-treated DU145 cells (n = 3). Representative micrographs of the fulvestrant- and ethanol-treated cell cultures with scratches at 0 h and after 16 h are shown. The wound is marked by dotted lines. (E) Fulvestrant inhibits transwell migration (left panel) and invasion (right panel) in DU145 cells (n = 3) after 5 hrs of fulvestrant treatment. (F) Reductions of filopodial cells and cells with intense stress fibers by fulvestrant (treated with 48 hrs) via an ERβ-dependent mechanism. Representative micrographs and the percentages of the cells with intense stress fibers and the filopodial cells (n = 3) are presented. Student t-test was performed to determine significance with a cutoff p value of 0.05. ** p<0.01; bars = S.D.