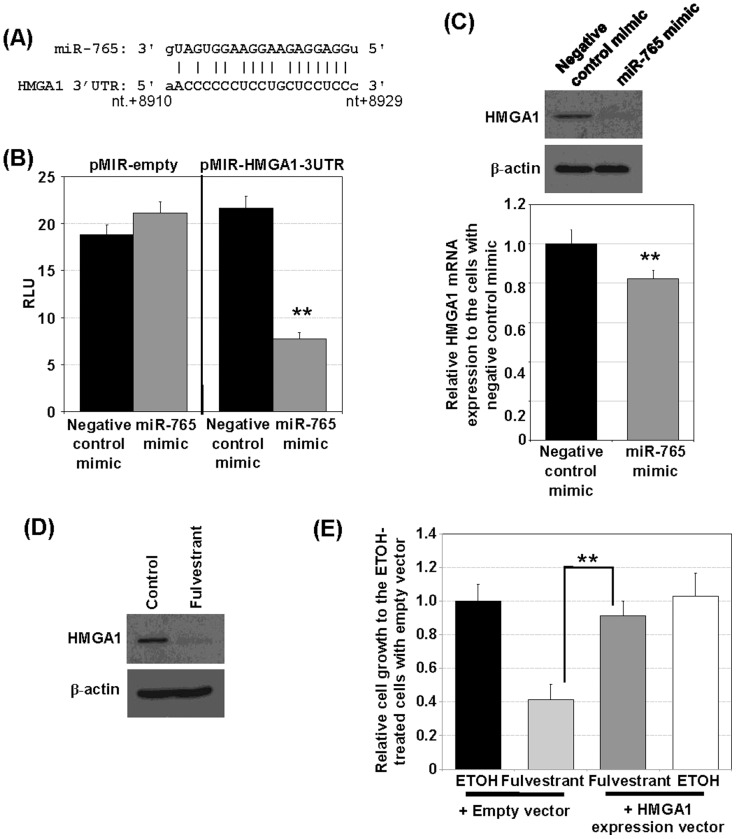
Figure 5. HMGA1 is a direct target of hsa-miR-765.
(A) The 3′UTR of HMGA1 from +8910 to +8929 is predicted to be hsa-miR-765 binding site. (B) Hsa-miR-765 interacts with 3′UTR of HMGA1 in a targeting reporter assay. DU145 cells were transfected with either pMIR-empty or pMIR-HMGA1-3UTR in which 3′ UTR of HMGA1 (+8026–+9332) was cloned into the 3′ end of luciferase. Reporter activities of the pMIR-HMGA1-3UTR transfected cells treated with hsa-miR-765 mimic or negative-control mimic are compared (n = 3). (C) Hsa-miR-765 mimic reduced HMGA1 protein expression in DU145 cells. Protein and mRNA levels of HMGA1 in the hsa-miR-765 mimic- and negative-control mimic-treated cells were determined by Western blot analysis (upper) and real-time RT-PCR analysis (lower), respectively. Results from miR-765 mimic vs negative control mimic are compared (n = 3). (D) Fulvestrant reduces HMGA1 protein expression in DU145 cells. Protein level of HMGA1 and β-actin in the fulvestrant-treated and ethanol-treated control (CTL) cells were determined by Western blot analysis. (E) Ectopic expression of HMGA1 blocks fulvestrant-induced DU145 cell growth inhibition. The relative cell growth was determined after 4 days of treatment with fulvestrant or ethanol after stable transfection of HMGA1 (or empty vector for control) for a week. Protein levels of HMGA1 were shown in Figure S6. The cell growth of fulvestrant-treated cells with HMGA1 overexpression vs empty vector are compared (n = 8). Student's t-test was performed to determine significance between groups using a cutoff p value of 0.05. **p<0.01; bar = S.D.