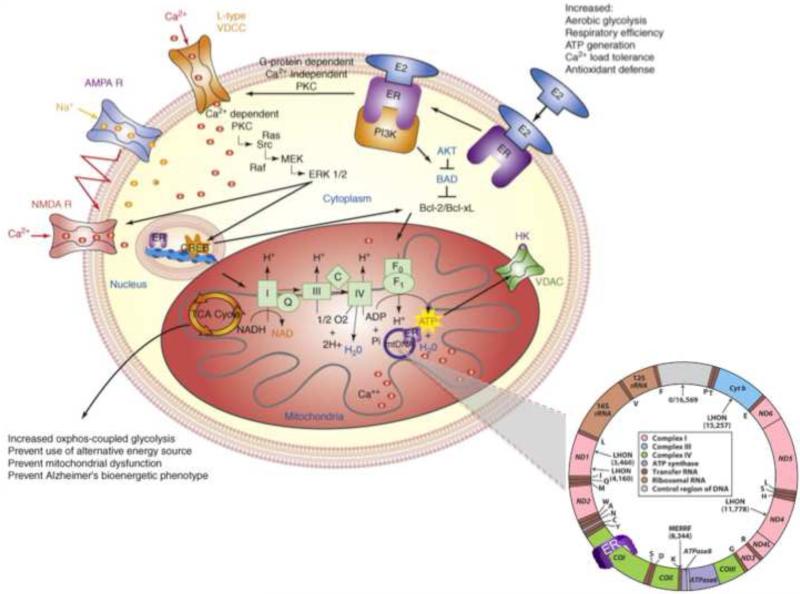
Figure 1. Estrogen regulation of intracellular brain metabolism pathways.
Estrogen-induced signaling pathways in hippocampal and cortical neurons converge upon the mitochondria to enhance glucose uptake and metabolism, aerobic glycolysis, tricarboxylic acid cycle (TCA)-coupled oxidative phosphorylation and ATP generation. In parallel, E2 increases antioxidant defense and antiapoptotic mechanisms. Estrogen receptors at the membrane, in mitochondria and within the nucleus are well positioned to regulate coordinated mitochondrial and nuclear gene expression required for optimal bioenergetics.